
The Earth–Sun orientation will change throughout the year as Earth revolves around the Sun. Using Figures 2-3 and 2-4 as models, sketch two similar diagrams for each date given to the right and below. First draw Earth’s axis and equator on the globe. Then, on the “sunny side” of the globe, draw a short line representing a flat surface at 66.5° N, 30° N, 0°, and 23.5° S, a stick figure at each site with the Sun’s rays striking the flat surface at the feet of the stick figure. On the profile view, draw the Sun’s rays striking the flat surface transcribing the angles that you drew on the globe.
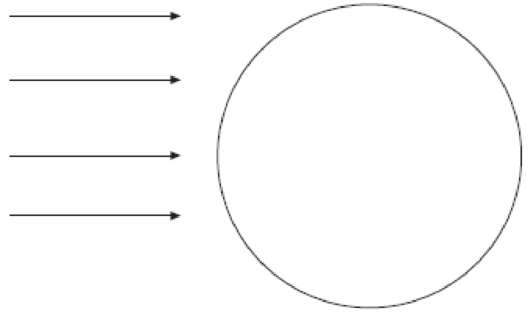
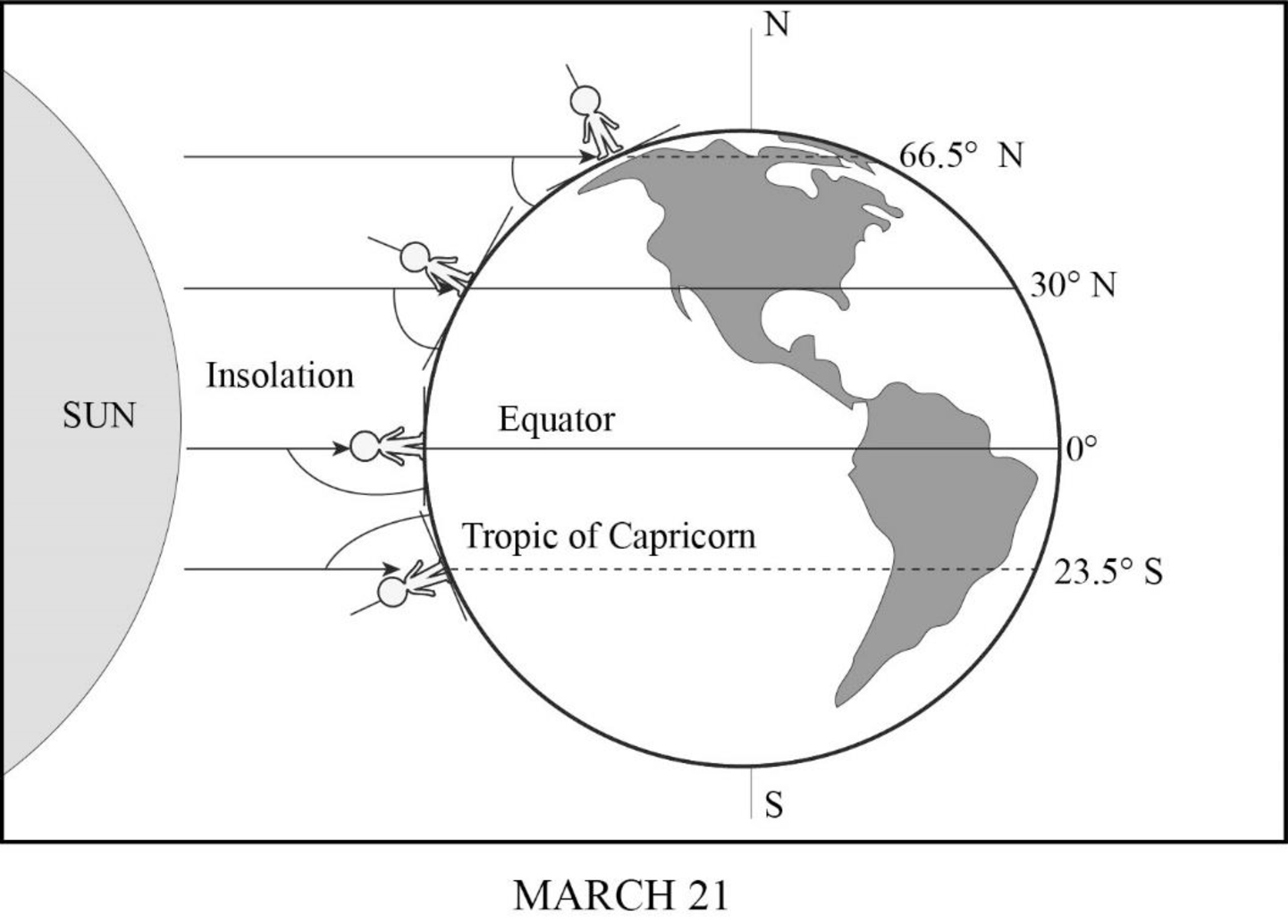
Sun’s rays striking Earth on March 21.
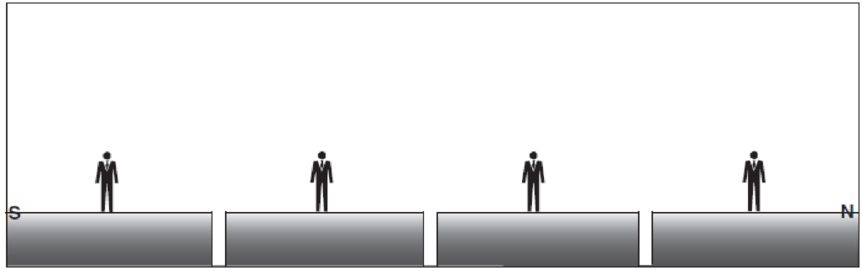
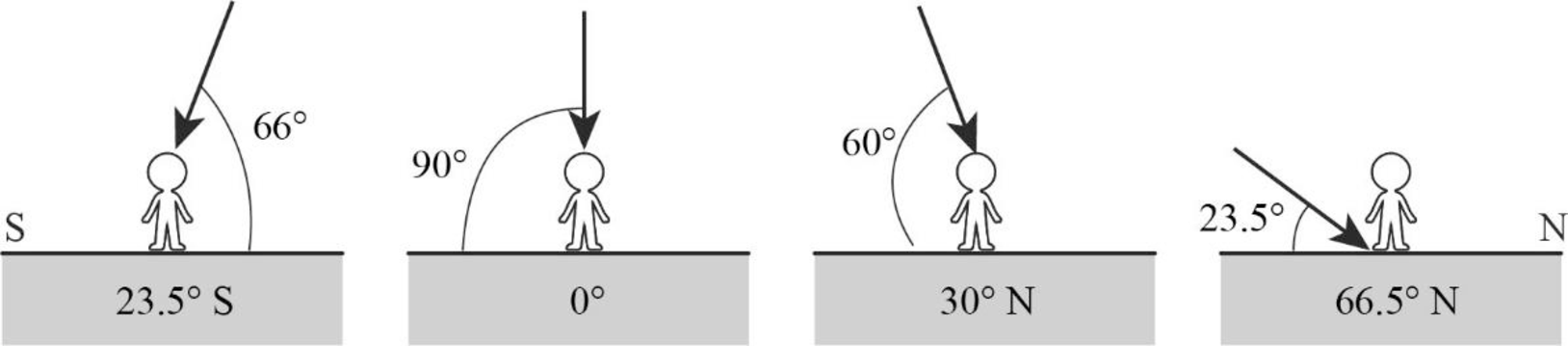
Profile view at Earth’s surface: solar noon on March 21.
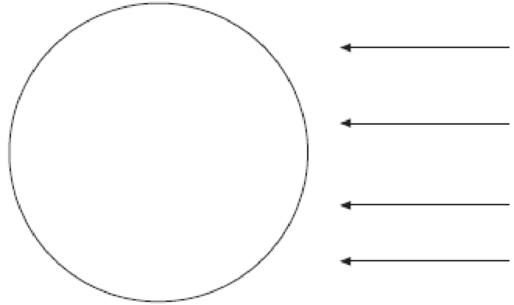
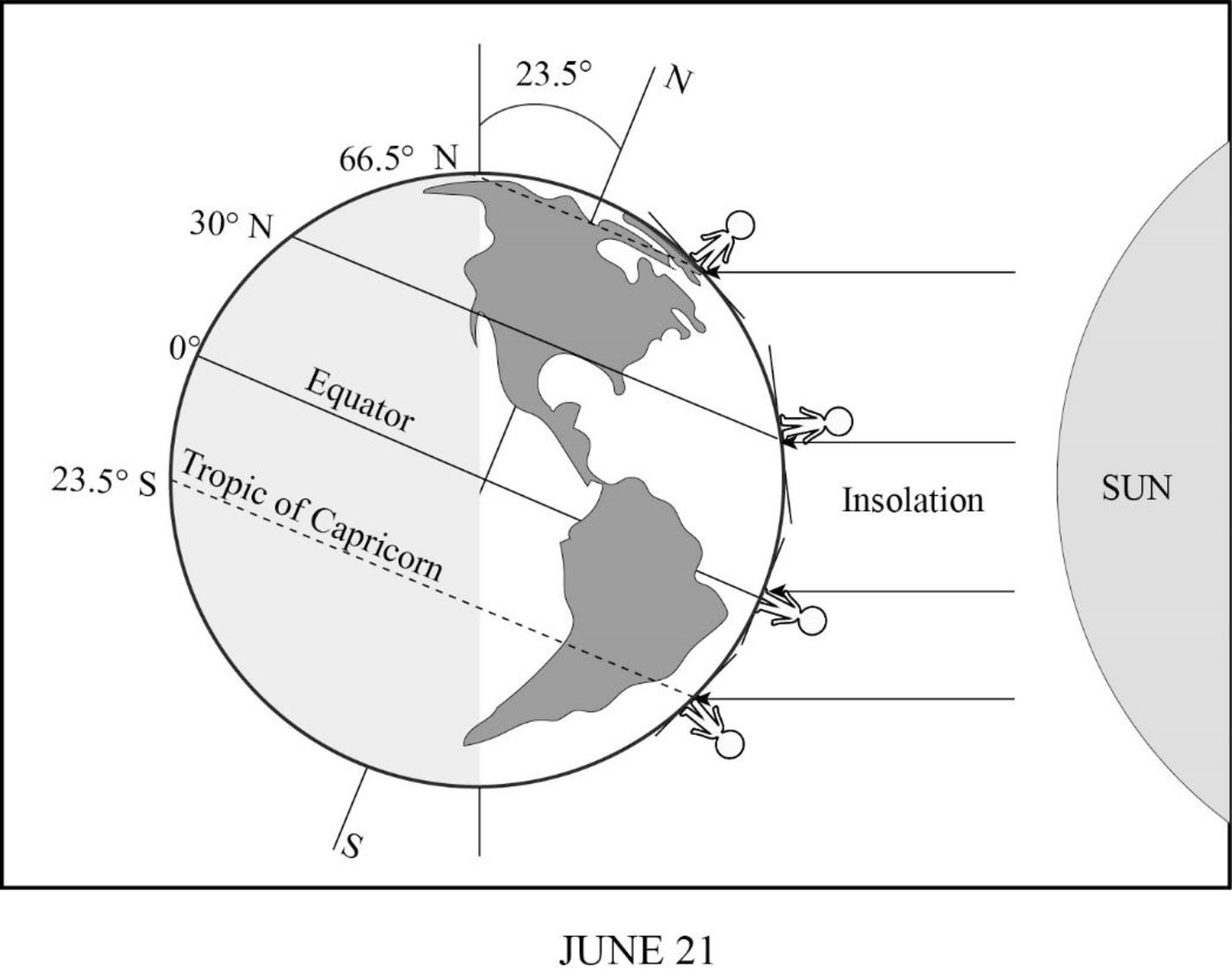
Sun’s rays striking Earth on June 21.
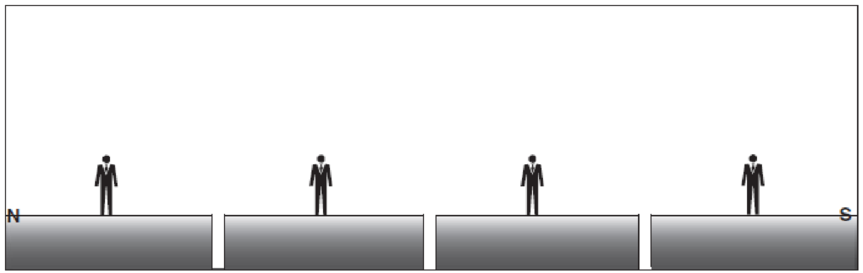
Profile view at Earth’s surface: solar noon on June 21.
Sketch representation of the incidence of the Sun’s rays on the images given in the question, on March 21 and June 21.
Answer to Problem 1E
On March 21, which is the time of vernal equinox on the Northern Hemisphere and autumn equinox in the Southern Hemisphere, there will be direct incidence of sunlight on the equator as well as on the other latitudes north and south of the equator. The figures given below represent the angle of incidence of insolation on various latitudes.
On June 21, which is the time of Summer Solstice in the Northern Hemisphere, the Sun will be more direct over the Northern Hemisphere, indicating the beginning of Summer season. The North Pole will be inclined at an angle of
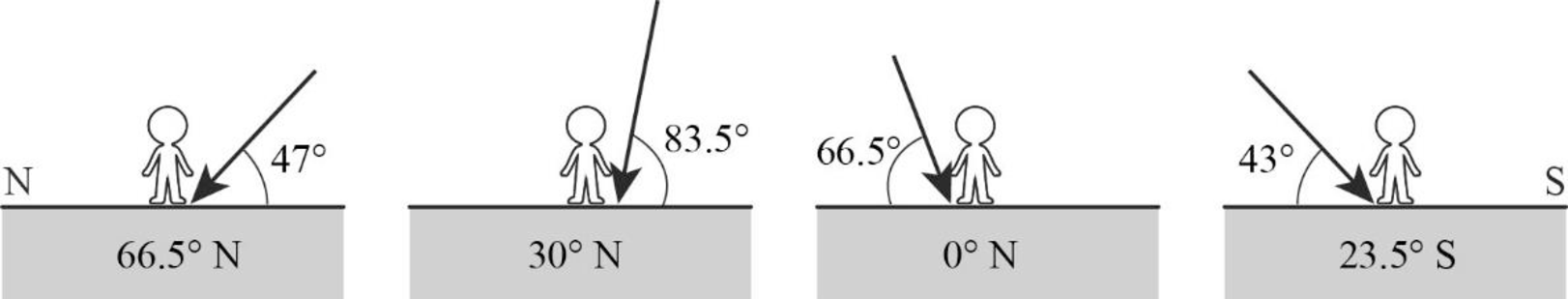
Explanation of Solution
On March 21, the Earth exhibits an equinox time. It is generally known as vernal equinox in the Northern hemisphere, while in the Southern Hemisphere, it is known as autumn equinox. During equinox, neither of the poles would be specifically inclined toward the Sun nor would any of the poles be receiving more insolation. Instead, both the hemispheres will experience equal duration of day and night. The insolation might fall on the Earth vertically, which means the equator along with latitudes above and below it receives vertical rays of the Sun.
June 21 is referred to as the June Solstice or Summer Solstice in the Northern Hemisphere. Solstice is the time during which one of the hemispheres will be facing the Sun more directly. During June Solstice, the Earth’s rotation axis over the North Pole is most directed or inclined (by nearly
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- ACTIVITY 10.2 Principle of Superposition Pg 170Assume that the playing cards shown in Figure 10.4 are layers of sedimentary rocks viewed from above. 1. In the space provided in Figure 10.4, list the cards by number, according to the order in which they appear to have been laid down. 2,9 4,1 7,3 6,10 2. Were you able to place all of the cards in sequence? Explain. 3. Apply the law of superposition to determine the relative ages of the sedimentary strata labeled A-D in Figure 10.5.arrow_forwardwrite one paragraph about the geology of Central Park In manhattan new york . use citations. thanks :)arrow_forward5. a. the Earth b. the Moon c. the Sun. d. the stars Water Vapolis is the gas form of water. liquid 6. When water evaporates, it changes from a into a gas. 7. Walking to school on a Spring day, Violet notices dew on the ground. On her way home, the dew has disappeared. What most likely has happened to the water? 3. Based on your knowledge of the water cycle, from what body of water does the most water evaporate? Why? What is the role of plants in the water cycle?arrow_forward
- 田 2, 3, 44 together = Chlorine 12) Filtration usty Sanda Gravel (10 5,6, +7 together = :: Aeration Tank :: Bar Screens :: Disinfection if no tertiary treatment :: Disinfection with tertiary treatment :: Grit Chamber Primary Sedimentation Tank :: Primary Treatment :: Raw Sewage :: River :: Secondary Sedimentation Tank Secondary Treatment Sludge Treatment :: Tertiary Treatment :: Treated Effluentarrow_forwardA 40-cm circular PPC pile is driven to a depth of 20 meters in the soil conditions shown below. Calculate the (a) shaft resistance in the clay layer using the alpha method and the (b) shaft resistance in the sand layer using the beta method. Depth (m) 14 20 30 Stiff Clay y = 19.8 kN/m³ Su = 130 kPa a = 0.58 20- Dense Sand y = 18.8 kN/m³ Q=35º 8 = 2/34arrow_forwardFigure 12.7: A. B.arrow_forward
- A. B. C. D. E.arrow_forwardA) List and describe the six stages that led to the formation of Earth. 1. Nebular stage Gravity caused collapse of a rotating mass of dust and gas. 2. A star forms 3. Planetesimals form 4. The Sun ignites 5. Inner planets 6. Outer planets B) What does the presence of banded iron formation tell us about conditions in the early atmosphere and oceans? (Short answer , couple of sentences) C)What does the sediment core from Walvis Ridge, southern Atlantic Ocean, from 55-56 million years ago tell us about past climate? (Short answer , couple of sentences )arrow_forwardA) List three things that can be measured from annual layers of ice cores. 1 2 3.arrow_forward
- 1. Use the descriptions of shoreline features provided above to label the structures in Figures 12.5 and 12.6. The same feature may appear more than once. 2. Next to each of the features listed below, indicate whether it is the result of erosional or depositional processes.Sea stack: Wave-cut cliff:Spit:Barrier island:Baymouth bar:Marine terrace:arrow_forwardActivity 12.5B: Identifying Shoreline Features on a Topographic Map Pg 209The area shown on the Point Reyes, California, topographic map is located directly to the southwest of the San Andreas Fault, in a very tectonically active region (Figure 12.10). As a result, some of this region has recently been uplifted and exhibits characteristics of an emergent coastline. On the other hand, because of the general rise in sea level over the past several thousand years, other areas exhibit features associated with submergent coastlines. Refer to this topographic map to complete the following. 1. What type of shoreline feature is Drakes Estero (located near the center of the map)? 2. Point Reyes, located in the bottom-left corner of the map, is a headland undergoing severe wave erosion. What type of feature is Chimney Rock, located off the shore of Point Reyes? 3. Several depositional features near Drakes Estero are related to the movement of sediment by longshore currents. What type of…arrow_forwardActivity 12.3: Wave Refraction Pgs 202-203Figure 12.2 is a map view of a headland along a coastline. The water depths are shown by blue contour lines. As you complete the following questions, assume that waves with a wavelength of 60 feet are approaching the shoreline from the bottom left of the figure. 1. At approximately what water depth-10, 20, 30, or 40 feet-will the approaching waves begin to touch bottom and slow down? (Hint: Recall that this occurs when the water depth is one-half the wavelength.) 2. Using the wave shown in Figure 12.2 as a starting point, sketch a series of lines to illustrate the wave refraction that will occur as the wave approaches the shore by following these steps:Step 1: Mark the position on the 30-foot contour line where the wave front will first touch bottom.Step 2: Knowing that the section of the wave that touches bottom will slow down first, sketch the shape of the wave front when it reaches the 20-foot contour line.Step 3: Using the same…arrow_forward
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





