Sample bartleby Q&A Solution
You ask questions, our tutors answer
Browse
Question
Calculate the frequency of heterozygotes in a population where 9% of the individuals have the recessive trait, i.e., red hair.
Expert Answer
According the Hardy-Weinberg Principle, the allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of other evolutionary influences.
For a single locus with two alleles, A and a, with their respective frequencies f(A) = p and f(a) = q, the expected genotype frequencies under random mating will be f(AA) = p2 for the AA homozygotes, f(aa) = q2 for the aa homozygotes, and f(Aa) = 2pq for the heterozygotes. In the absence of selection, mutation, etc., allele frequencies p and q are constant between generations, so equilibrium is reached.
Hence, the Hardy-Weinberg Equation is derived as:
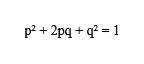
Let the dominant trait be p and the recessive trait be q. 9% of the individuals are red-haired. So, according to Hardy-Weinberg Principle,
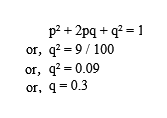
Thus, the value of p2 is as follows:
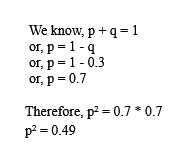
The frequency of heterozygotes is denoted by 2pq.
Hence,
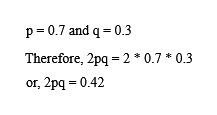
The frequency of heterozygous individual is 0.42.