1 5 7 9 10 NOT 6 11 12 3 4 6 NOT 7 9 OR 11 6 10 AND 7 х OR NOT3AND Z 5 OR NOT 2 OR Y AND 1 AND 4 1 Y 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 C 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 C 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 Boolean Identities Identity Name Identity Law Null (or Dominance) Law AND Form OR Form 1*= x 0+X= X 1+X 1 Ox= 0 Idempotent Law XX %3D х X+X X xX = 0 X+X= 1 Inverse Law X+y y+x (X+y)+z = x+(y+z Commutative Law ху %3D ух (ху)z %3D x(уz) |X+yz = (x+y)(x+z) x(y+z) = xy+xz x(x+у) — х (xy) = X+7 Associative Law Distributive Law X+ху%3D х (X+y) = xy X = x Absorption Law DeMorgan's Law Double Complement Law
1 5 7 9 10 NOT 6 11 12 3 4 6 NOT 7 9 OR 11 6 10 AND 7 х OR NOT3AND Z 5 OR NOT 2 OR Y AND 1 AND 4 1 Y 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 C 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 C 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 Boolean Identities Identity Name Identity Law Null (or Dominance) Law AND Form OR Form 1*= x 0+X= X 1+X 1 Ox= 0 Idempotent Law XX %3D х X+X X xX = 0 X+X= 1 Inverse Law X+y y+x (X+y)+z = x+(y+z Commutative Law ху %3D ух (ху)z %3D x(уz) |X+yz = (x+y)(x+z) x(y+z) = xy+xz x(x+у) — х (xy) = X+7 Associative Law Distributive Law X+ху%3D х (X+y) = xy X = x Absorption Law DeMorgan's Law Double Complement Law
Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course List)
12th Edition
ISBN:9781285867168
Author:Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Chapter4: Software: Systems And Application Software
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 14SAT: A(n) ______ converts a programmers source code into the machine-language instructions consisting of...
Related questions
Question
Form boolean equations in POS and SOP forms from the truth table attached (PLEASE EXPLAIN ALL STEPS), then show steps to simplify using boolean identities (also attached).
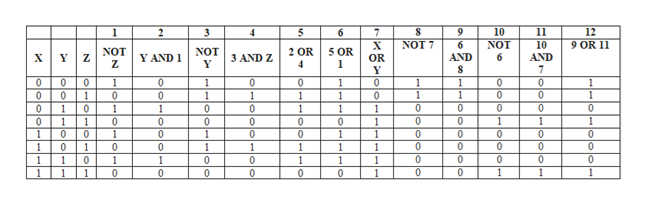
Transcribed Image Text:1
5
7
9
10
NOT
6
11
12
3
4
6
NOT 7
9 OR 11
6
10
AND
7
х
OR
NOT3AND Z
5 OR
NOT
2 OR
Y AND 1
AND
4
1
Y
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
C
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
C
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
1
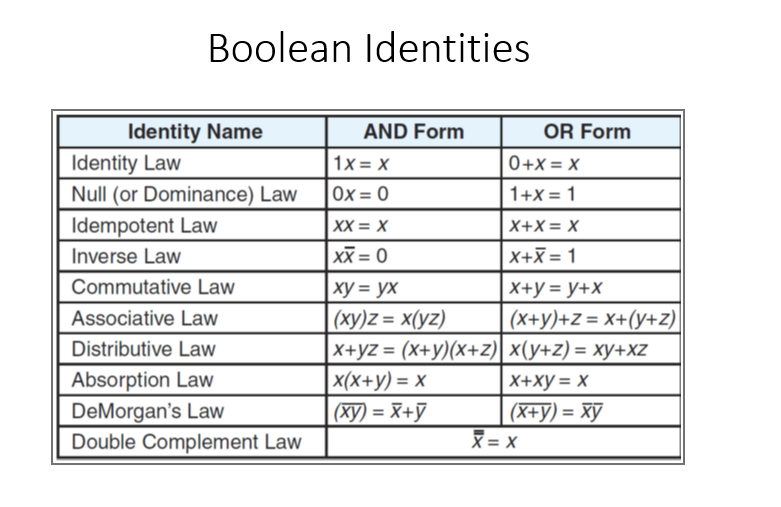
Transcribed Image Text:Boolean Identities
Identity Name
Identity Law
Null (or Dominance) Law
AND Form
OR Form
1*= x
0+X= X
1+X 1
Ox= 0
Idempotent Law
XX %3D х
X+X X
xX = 0
X+X= 1
Inverse Law
X+y y+x
(X+y)+z = x+(y+z
Commutative Law
ху %3D ух
(ху)z %3D x(уz)
|X+yz = (x+y)(x+z) x(y+z) = xy+xz
x(x+у) — х
(xy) = X+7
Associative Law
Distributive Law
X+ху%3D х
(X+y) = xy
X = x
Absorption Law
DeMorgan's Law
Double Complement Law
Expert Solution
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 10 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285867168
Author:
Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Information Systems (MindTap Course…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285867168
Author:
Ralph Stair, George Reynolds
Publisher:
Cengage Learning