1² + b² = 4) and (4 – a² – b² = c), and planes (a = 0), (b = 0), and (c = 4) bound a solid octant. With a density function of f (a,b, c) = a + b, set up an iterated triple integral equal s of the solid. Use rectangular coordinates.
1² + b² = 4) and (4 – a² – b² = c), and planes (a = 0), (b = 0), and (c = 4) bound a solid octant. With a density function of f (a,b, c) = a + b, set up an iterated triple integral equal s of the solid. Use rectangular coordinates.
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Chapter10: Analytic Geometry
Section10.1: The Rectangular Coordinate System
Problem 41E: Find the exact lateral area of each solid in Exercise 40. Find the exact volume of the solid formed...
Related questions
Question
Please help me to answer this.
Thank you!
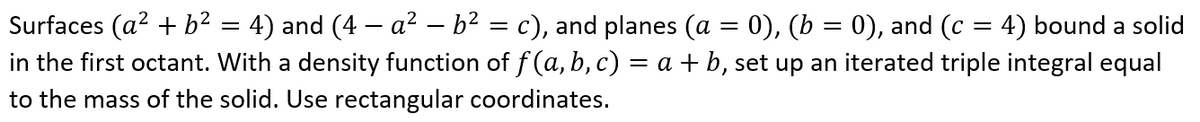
Transcribed Image Text:Surfaces (a2 + b² = 4) and (4 – a² – b² = c), and planes (a = 0), (b = 0), and (c :
in the first octant. With a density function of f (a, b, c) = a + b, set up an iterated triple integral equal
4) bound a solid
to the mass of the solid. Use rectangular coordinates.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,