1 S = 1 + dx y dx = 2n ---Select--- v 1 + 1 dx x + 1 00 = 2n dx ---Select--- v Rather than trying to evaluate this integral, note the following. V x4 + 1 ? v Vx4 = x for x > 0 Thus, if the area is finite, we have the following. x4 + 1 o y2 dx = 2n S = 2n dx ? v 2n dx /1 Ji But we know that this integral ---Select--- v so the area S is infinite. 118
1 S = 1 + dx y dx = 2n ---Select--- v 1 + 1 dx x + 1 00 = 2n dx ---Select--- v Rather than trying to evaluate this integral, note the following. V x4 + 1 ? v Vx4 = x for x > 0 Thus, if the area is finite, we have the following. x4 + 1 o y2 dx = 2n S = 2n dx ? v 2n dx /1 Ji But we know that this integral ---Select--- v so the area S is infinite. 118
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Chapter9: Surfaces And Solids
Section9.3: Cylinders And Cones
Problem 6E: Suppose that r=12 cm and h=15 cm in the right circular cylinder. Find the exact and approximate a...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The surface formed by rotating the curve y = , x 2 1, about the x-axis is known as Gabriel's horn. Show that the surface area is infinite (although the enclosed volume is
finite).
2
dy
1 +
dx
S =
dx
---Select--- v
1 +
1
dx
= 2n
x* + 1
= 2n
dx
---Select--- v
Rather than trying to evaluate this integral, note the following.
Vx4 + 1 ? v
X4 = x2 for x > 0
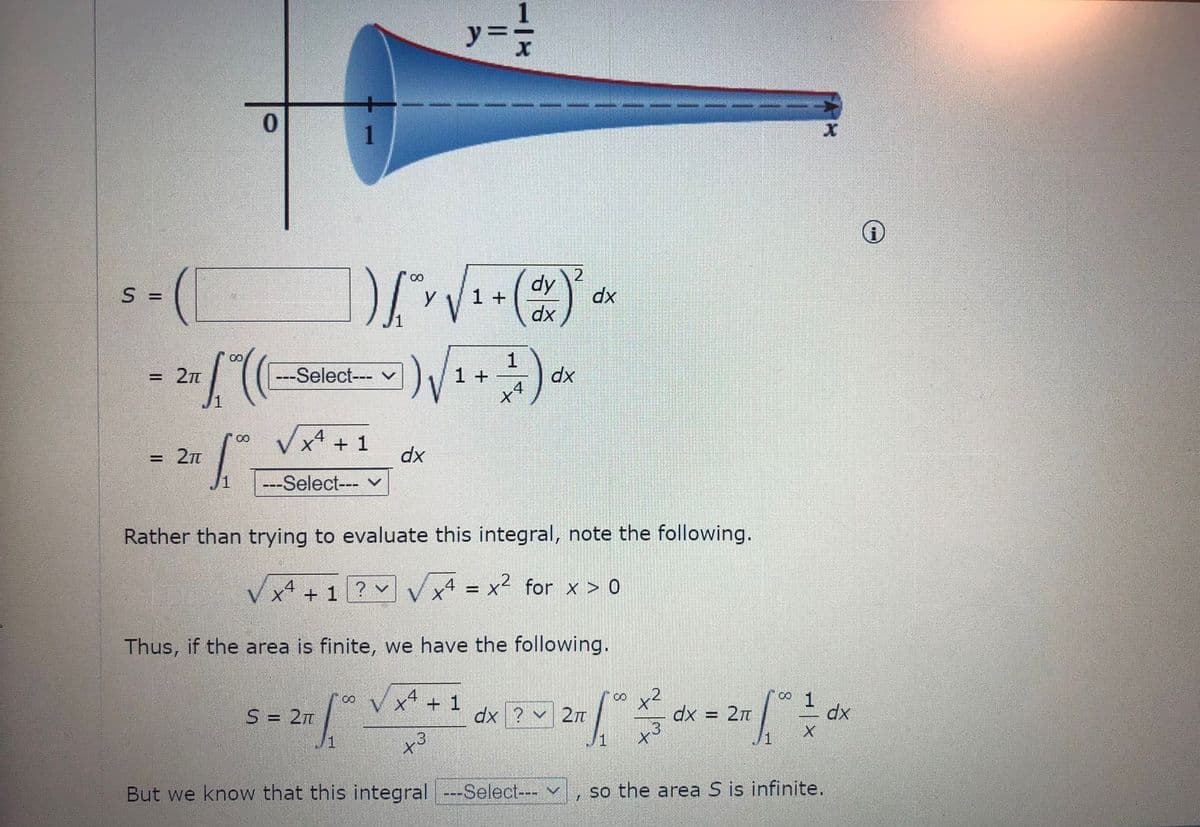
Transcribed Image Text:y =-
1
dy
1 +
dx
%3D
dx
1
---Select---
1 +
dx
%3D
x4
4
+ 1
= 2n
dx
---Select--- v
Rather than trying to evaluate this integral, note the following.
Vx4 + 1 ? v
4 = x2 for x > 0
Thus, if the area is finite, we have the following.
x* + 1
o x2
dx = 2m
S = 2n
dx ? v 2TT
dx
%3D
But we know that this integral --Select--- ▼
so the area S is infinite.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,