1. Draw a sketch of the physical situation with all given physical quantities clearly labeled. Show the path the laser follows until it reaches surface B in your sketch (do not make any assumptions about what will happen to the path of the laser after it reaches surface B in this sketch). 2. Determine the angle (from the normal) with which the laser hits surface B. Clearly show all steps, starting from generalized equations. Explain your mathematical work in words. Your explanation should cover both what you did and the thought process behind why you did that. 3. Draw a ray diagram which represents the path the light takes after it is incident on surface B. Include any reflected and refracted rays that exist in your ray diagram. Determine the angle(s) of this/(these) ray(s) with respect to the normal at surface B. Explain any mathematical work needed to complete the ray diagram in words. Your explanation should cover both what you did and the thought process behind why you did that. (you do not need to follow through with any subsequent reflections or refractions that may or may not occur after surface B) 4. Evaluate your answers. Consider all aspects of your answer (the numerical value, sign, units, behavior, etc) in your evaluation.
1. Draw a sketch of the physical situation with all given physical quantities clearly labeled. Show the path the laser follows until it reaches surface B in your sketch (do not make any assumptions about what will happen to the path of the laser after it reaches surface B in this sketch). 2. Determine the angle (from the normal) with which the laser hits surface B. Clearly show all steps, starting from generalized equations. Explain your mathematical work in words. Your explanation should cover both what you did and the thought process behind why you did that. 3. Draw a ray diagram which represents the path the light takes after it is incident on surface B. Include any reflected and refracted rays that exist in your ray diagram. Determine the angle(s) of this/(these) ray(s) with respect to the normal at surface B. Explain any mathematical work needed to complete the ray diagram in words. Your explanation should cover both what you did and the thought process behind why you did that. (you do not need to follow through with any subsequent reflections or refractions that may or may not occur after surface B) 4. Evaluate your answers. Consider all aspects of your answer (the numerical value, sign, units, behavior, etc) in your evaluation.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:1. Draw a sketch of the physical situation with all given physical quantities clearly labeled. Show the path the laser
follows until it reaches surface B in your sketch (do not make any assumptions about what will happen to the path
of the laser after it reaches surface B in this sketch).
2. Determine the angle (from the normal) with which the laser hits surface B. Clearly show all steps, starting from
generalized equations. Explain your mathematical work in words. Your explanation should cover both what you did
and the thought process behind why you did that.
3. Draw a ray diagram which represents the path the light takes after it is incident on surface B. Include any reflected
and refracted rays that exist in your ray diagram. Determine the angle(s) of this/(these) ray(s) with respect to the
normal at surface B. Explain any mathematical work needed to complete the ray diagram in words. Your explanation
should cover both what you did and the thought process behind why you did that. (you do not need to follow
through with any subsequent reflections or refractions that may or may not occur after surface B)
4. Evaluate your answers. Consider all aspects of your answer (the numerical value, sign, units, behavior, etc) in your
evaluation.
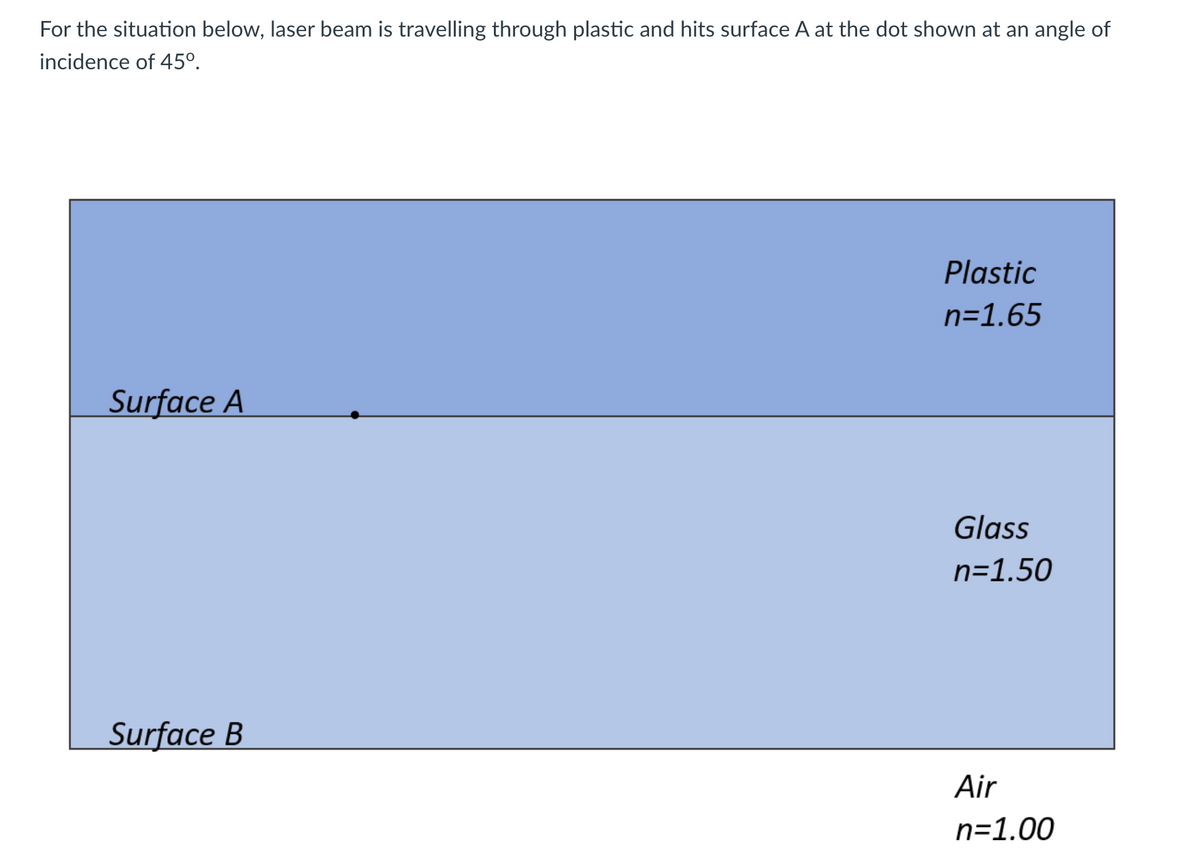
Transcribed Image Text:For the situation below, laser beam is travelling through plastic and hits surface A at the dot shown at an angle of
incidence of 45°.
Plastic
n=1.65
Surface A
Glass
n=1.50
Surface B
Air
n=1.00
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images
