1. What are the differences between the germanium and silicon diodes? • (5) None of the above is true. 2. How does the diode behave as the supply voltage carries? (2) In forward biasing the current is very low, until the voltage reaches a characteristic value for the diode, then it increases exponentially. In reverse biasing the current is extremely low, and is difficult to measure. 3. What is the threshold voltage for the diodes D₁ and D₂? • (3) 0.2-0.3 V for D2 and 0.5-0.7 V for D₁. 4. Which of these is the symbol for a diode? • (2) 5. Does the voltage-current characteristic of the diode depend on both the temperature and the type of semiconductor? • (3) Yes
1. What are the differences between the germanium and silicon diodes? • (5) None of the above is true. 2. How does the diode behave as the supply voltage carries? (2) In forward biasing the current is very low, until the voltage reaches a characteristic value for the diode, then it increases exponentially. In reverse biasing the current is extremely low, and is difficult to measure. 3. What is the threshold voltage for the diodes D₁ and D₂? • (3) 0.2-0.3 V for D2 and 0.5-0.7 V for D₁. 4. Which of these is the symbol for a diode? • (2) 5. Does the voltage-current characteristic of the diode depend on both the temperature and the type of semiconductor? • (3) Yes
Related questions
Question
Give a explanation what happen in the result

Transcribed Image Text:1. What are the differences between the germanium and silicon diodes?
• (5) None of the above is true.
2. How does the diode behave as the supply voltage carries?
(2) In forward biasing the current is very low, until the voltage reaches a
characteristic value for the diode, then it increases exponentially. In reverse
biasing the current is extremely low, and is difficult to measure.
3. What is the threshold voltage for the diodes D₁ and D2?
(3) 0.2-0.3 V for D2 and 0.5-0.7 V for D₁.
4. Which of these is the symbol for a diode?
•(2)
5. Does the voltage-current characteristic of the diode depend on both the temperature
and the type of semiconductor?
•(3) Yes
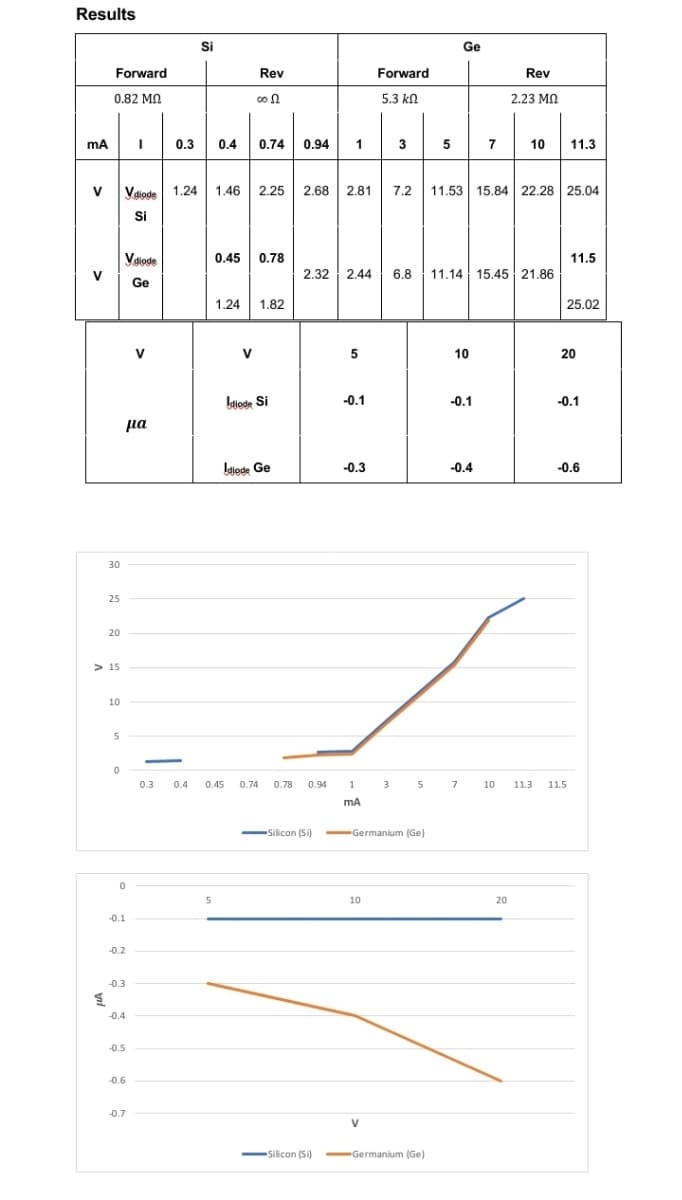
Transcribed Image Text:Results
mA
V
Forward
0.82 ΜΩ
S
30
25
20
>15
10
5
0
0
-0.1
-0.2
-0.3
Vdiode 1.24 1.46 2.25
Si
-0.4
Vdiode
Ge
-0.5
I
-0.6
-0.7
V
μα
-
Si
0.3
0.3 0.4
5
Rev
0052
0.74
0.45 0.78
0.4 0.45
1.24 1.82
V
Idiode Si
Idiode Ge
0.94 1
0.74 0.78 0.94
-Silicon (Si)
5
-0.1
-0.3
2.68 2.81 7.2 11.53 15.84 22.28 25.04
1
mA
Forward
5.3 ΚΩ
2.32 2.44 6.8 11.14 15.45 21.86
10
3
V
3
-Germanium (Ge)
5
5
Silicon (Si) -Germanium (Ge)
Ge
10
-0.1
7
-0.4
7
Rev
2.23 ΜΩ
10 11.3
20
11.5
25.02
20
-0.1
10 11.3 11.5
-0.6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 4 images
