1. Writing the Navier-Stokes Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates Consider a point (x, y, z) in three-dimensional space. We project the point onto the ry plane, and connect the projected point in the plane, say A, to the origin. The angle that the ray connecting A to the origin makes with the r axis is 0, and its length is r. Then, x = r cos 0, y =r sin 0, and z remains unchanged, z = z. These constitute the cylindrical coordinates. (a) Use chain rule of differentiation to show that sin 0 (cos 0) Or cos e + ar (sin 0) and, of course, 0/dz does not change. (b) Write down the Navier-Stokes equation in Cartesian coordinates, and using (a) rewrite it in cylindrical coordinates.
1. Writing the Navier-Stokes Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates Consider a point (x, y, z) in three-dimensional space. We project the point onto the ry plane, and connect the projected point in the plane, say A, to the origin. The angle that the ray connecting A to the origin makes with the r axis is 0, and its length is r. Then, x = r cos 0, y =r sin 0, and z remains unchanged, z = z. These constitute the cylindrical coordinates. (a) Use chain rule of differentiation to show that sin 0 (cos 0) Or cos e + ar (sin 0) and, of course, 0/dz does not change. (b) Write down the Navier-Stokes equation in Cartesian coordinates, and using (a) rewrite it in cylindrical coordinates.
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
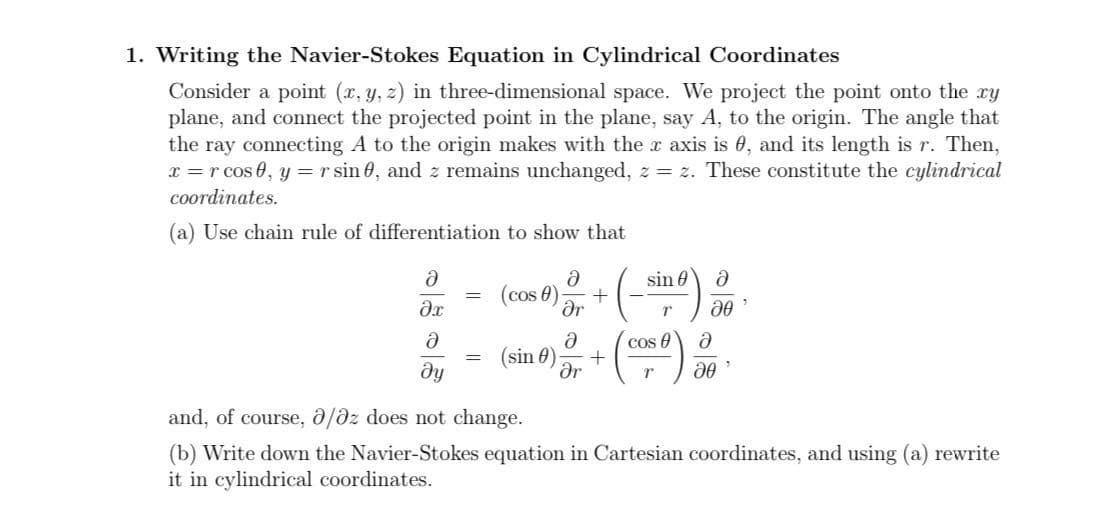
Transcribed Image Text:1. Writing the Navier-Stokes Equation in Cylindrical Coordinates
Consider a point (x, y, z) in three-dimensional space. We project the point onto the ry
plane, and connect the projected point in the plane, say A, to the origin. The angle that
the ray connecting A to the origin makes with the r axis is 0, and its length is r. Then,
x = r cos 0, y =r sin 0, and z remains unchanged, z = z. These constitute the cylindrical
coordinates.
(a) Use chain rule of differentiation to show that
sin 0
(cos 0)
Or
cos e
+
ar
(sin 0)
and, of course, 0/dz does not change.
(b) Write down the Navier-Stokes equation in Cartesian coordinates, and using (a) rewrite
it in cylindrical coordinates.
Expert Solution
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 10 steps with 17 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The