1.7-2 In the mean-value theorem for derivatives, Theorem 1.6, let f(x) = x?. Find the point & specified by the theorem and verify that this point lies in the interval (a,b).
1.7-2 In the mean-value theorem for derivatives, Theorem 1.6, let f(x) = x?. Find the point & specified by the theorem and verify that this point lies in the interval (a,b).
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.5: The Kernel And Range Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 30EQ
Related questions
Question
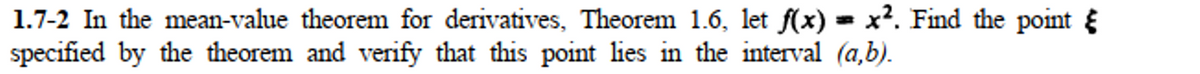
Transcribed Image Text:1.7-2 In the mean-value theorem for derivatives, Theorem 1.6, let f(x) = x². Find the point {
specified by the theorem and verify that this point lies in the interval (a,b).
![Theorem 1.6: Mean-value theorem for derivatives If f(x) is continuous
on the (closed and finite) interval [a,b] and differentiable on (a, b),
1.7 SOME MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 27
then
(b) – f(a)
b — а
= f'(E)
for some { E (a, b)
(1.29)](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F4d060456-6ac0-4f8c-9fca-77f248c981aa%2Fc2b4b736-6ec9-42c9-94c2-c0f3419e1f83%2Fja4wdds_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Theorem 1.6: Mean-value theorem for derivatives If f(x) is continuous
on the (closed and finite) interval [a,b] and differentiable on (a, b),
1.7 SOME MATHEMATICAL PRELIMINARIES 27
then
(b) – f(a)
b — а
= f'(E)
for some { E (a, b)
(1.29)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage