10kN 5kN/m 1m 2m 2m
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Draw shear force and bending moment diagrams for the given simply supported beam.
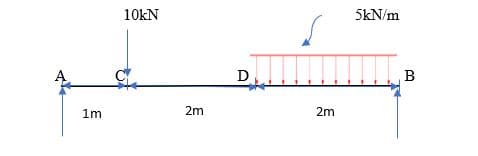
Transcribed Image Text:10kN
5kN/m
1m
2m
2m
Expert Solution
Step 1
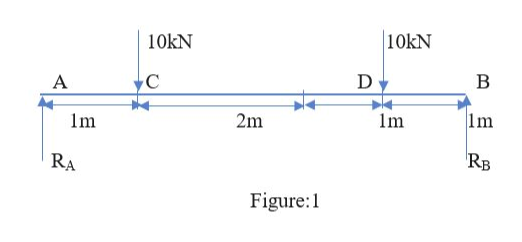
Draw a free body diagram converting the UDL into a point load
As UDL is given 5kn and it is acting on the 2m length
Therefore, load will be 5 x 2 = 10 kN acting on center of 1m from point B.
Step 2
Take moments @A, we know the condition
Anticlockwise moment = clockwise moments
We know moment = force x perpendicular distance
RB x 5 = (10 x 1) + (10 x 4)
RB x 5 = 50
RB = 50/5= 10 kN.
Summation of upward force = summation of downward force
RA + RB = 10+10
RA + 10 = 20
RA = 20 – 10
RA = 10 kN
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning