15. (Physics) Figure 7.16 shows a harmonic oscillator, which consists of an object of mass, m, attached to one end of a spring. The spring's other end is attached to a wall, and the object is free to slide over a frictionless surface. Assuming the object is initially at rest (that is, the spring is neither stretched nor compressed) and then pulled to position A at time t = 0, the displace- ment of the mass at any other time, 1, is given by this formula: x = A cos (1 VEm) x is the displacement. k is the spring constant (N/m). m is the mass (kg). A is the initial displacement (cm). Assuming A is 10 centimeters, k is 150 N/m, and m is 200 kilograms, modify Program 7.13 to plot the displacement of the mass from / = 0 to t = 20 seconds in increments of 0.25 seconds. m X= -A X= 0 X = +A Figure 7.16 A harmonic oscillator
15. (Physics) Figure 7.16 shows a harmonic oscillator, which consists of an object of mass, m, attached to one end of a spring. The spring's other end is attached to a wall, and the object is free to slide over a frictionless surface. Assuming the object is initially at rest (that is, the spring is neither stretched nor compressed) and then pulled to position A at time t = 0, the displace- ment of the mass at any other time, 1, is given by this formula: x = A cos (1 VEm) x is the displacement. k is the spring constant (N/m). m is the mass (kg). A is the initial displacement (cm). Assuming A is 10 centimeters, k is 150 N/m, and m is 200 kilograms, modify Program 7.13 to plot the displacement of the mass from / = 0 to t = 20 seconds in increments of 0.25 seconds. m X= -A X= 0 X = +A Figure 7.16 A harmonic oscillator
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Chapter1: Computer Networks And The Internet
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem R1RQ: What is the difference between a host and an end system? List several different types of end...
Related questions
Question
C++ program
Please modify program to question 15
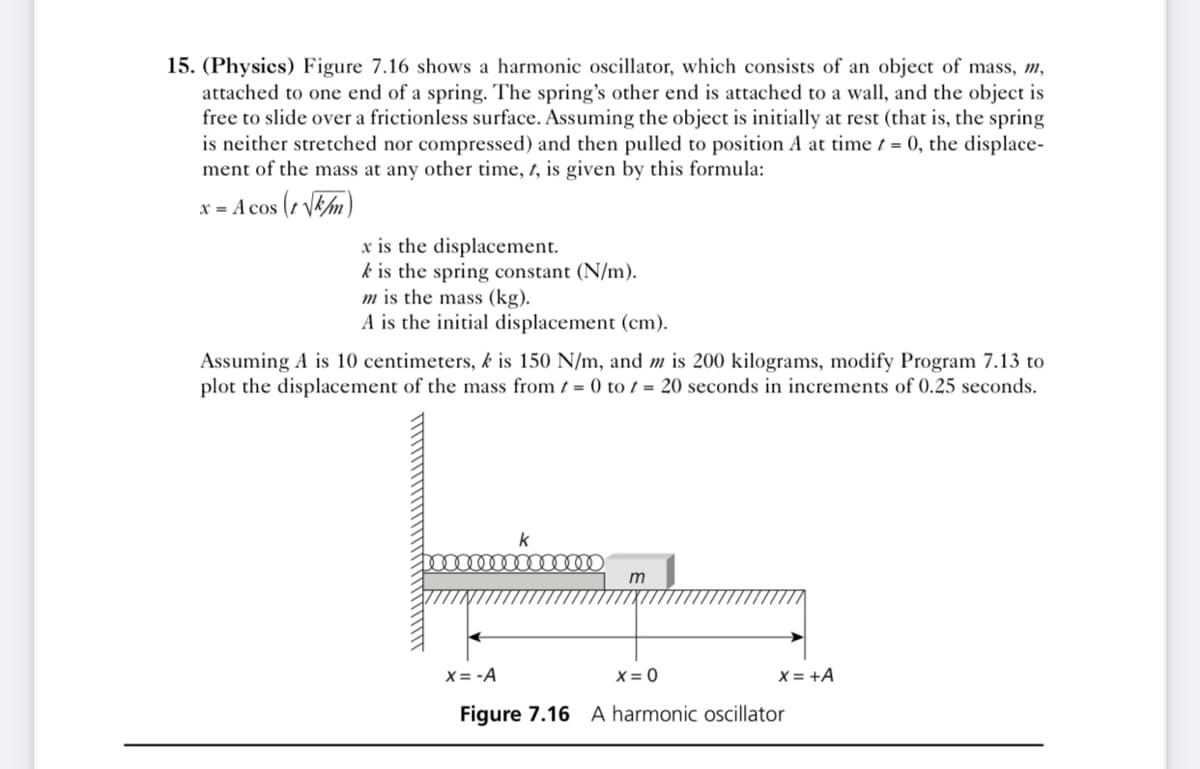
Transcribed Image Text:15. (Physics) Figure 7.16 shows a harmonic oscillator, which consists of an object of mass, m,
attached to one end of a spring. The spring's other end is attached to a wall, and the object is
free to slide over a frictionless surface. Assuming the object is initially at rest (that is, the spring
is neither stretched nor compressed) and then pulled to position A at time t = 0, the displace-
ment of the mass at any other time, 1, is given by this formula:
x = A cos (2 VEm)
x is the displacement.
k is the spring constant (N/m).
m is the mass (kg).
A is the initial displacement (cm).
Assuming A is 10 centimeters, k is 150 N/m, and m is 200 kilograms, modify Program 7.13 to
plot the displacement of the mass from t = 0 to t = 20 seconds in increments of 0.25 seconds.
m
X = -A
X = 0
X = +A
Figure 7.16 A harmonic oscillator
![Program 7.13
tinclude <iostream>
linclude <emath>
using namespace std;
int main()
const int MAXPOINTS = 100:
int i, npts, nval(MAXPOINTS];
double x, fval, ymin, ymax, width, sval[MAXPOINTS);
y axis";
char label0 - "
char axis[] = "+-
char line[] = "|
ymax - 1.0e-5;
ymin - 1.0e5;
width = 53;
// Load the data to be plotted and find the max and min values
i- 1;
for (x = -5.0; x <= 5.0; x += 0.5)
sval[i] = pow (x, 3.0);
if (sval[i] > ymax) ymax = sval[i];
if (sval(i) < ymin) ymin = sval[i];
i++;
if (i >= MAXPOINTS) break; // don't exceed the maximum points
npts = i - 1;
// Scale all the y values
for (i=1; i <= npts; i++)
fval = (sval[i] - ymin)/(ymax - ymin)* (width - 1) + 1;
nval[i] - fval + 0.5; // convert to an integer value
// Produce the plot
cout << "Minimum y value: " << ymin << endl;
cout << "Maximum y value: " << ymax << endl;
cout << label << endl;
cout << axis << endl;
Copyright 2012 Cengage Leaming All Righe Reservod. May not he copiod, cannod. or duplicated,in whole orin part. Due to clecic rights, some thind party content muy he ppreed tom the cllook andir Chupter.
Edtorial eview has doemed that any presed cmtet dees t materially allot the overal leaning enperiene. Cenpage Leaning reserves the rightte romeve alitinal ontonty timei vaegent rights rerictio require it
428 Arrays
for (i - 1; i <- npts; i++)
line[ (nval[i] + 2)] - *';
cout <« line << endl;
line[ (nval(i] + 2)) - ';
// set character to an asterisk
// output the line
// reset character to a blank
return 0;
Program 7.13 produces the following output:
Minimum y value: -125
Maximum y value: 125
y axis](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F9b4e3f5e-c418-473e-98f7-80dfb1b9a99b%2Faa3cf43e-4f71-43d5-9a55-957df72a3219%2F6zjg95_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Program 7.13
tinclude <iostream>
linclude <emath>
using namespace std;
int main()
const int MAXPOINTS = 100:
int i, npts, nval(MAXPOINTS];
double x, fval, ymin, ymax, width, sval[MAXPOINTS);
y axis";
char label0 - "
char axis[] = "+-
char line[] = "|
ymax - 1.0e-5;
ymin - 1.0e5;
width = 53;
// Load the data to be plotted and find the max and min values
i- 1;
for (x = -5.0; x <= 5.0; x += 0.5)
sval[i] = pow (x, 3.0);
if (sval[i] > ymax) ymax = sval[i];
if (sval(i) < ymin) ymin = sval[i];
i++;
if (i >= MAXPOINTS) break; // don't exceed the maximum points
npts = i - 1;
// Scale all the y values
for (i=1; i <= npts; i++)
fval = (sval[i] - ymin)/(ymax - ymin)* (width - 1) + 1;
nval[i] - fval + 0.5; // convert to an integer value
// Produce the plot
cout << "Minimum y value: " << ymin << endl;
cout << "Maximum y value: " << ymax << endl;
cout << label << endl;
cout << axis << endl;
Copyright 2012 Cengage Leaming All Righe Reservod. May not he copiod, cannod. or duplicated,in whole orin part. Due to clecic rights, some thind party content muy he ppreed tom the cllook andir Chupter.
Edtorial eview has doemed that any presed cmtet dees t materially allot the overal leaning enperiene. Cenpage Leaning reserves the rightte romeve alitinal ontonty timei vaegent rights rerictio require it
428 Arrays
for (i - 1; i <- npts; i++)
line[ (nval[i] + 2)] - *';
cout <« line << endl;
line[ (nval(i] + 2)) - ';
// set character to an asterisk
// output the line
// reset character to a blank
return 0;
Program 7.13 produces the following output:
Minimum y value: -125
Maximum y value: 125
y axis
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133594140
Author:
James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780124077263
Author:
David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:
Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337569330
Author:
Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781337093422
Author:
Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9780133750423
Author:
VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:
Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T…
Computer Engineering
ISBN:
9781119368830
Author:
FITZGERALD
Publisher:
WILEY