16.23. A gas is in equilibrium with a solid surface onto which its molecules can adsorb. The surface exposes M adsorption sites, each of which can be either free or occupied by a single gas molecule. Adsorbed molecules do not interact with each other, but there is a favorable energetic decrease of amount -e each time a site is осcupied. (a) Find the canonical partition function for N molecules adsorbed on M sites at a temperature T. (b) Find an expression for the chemical potential of an adsorbed molecule, µads- (c) At equilibrium at constant T, show that the dependence of the fraction of occupied sites, x = N/M, is given by the so-called Langmuir adsorption %3D isotherm, cP X = 1+ cP where c is a constant. How does c vary with temperature?
16.23. A gas is in equilibrium with a solid surface onto which its molecules can adsorb. The surface exposes M adsorption sites, each of which can be either free or occupied by a single gas molecule. Adsorbed molecules do not interact with each other, but there is a favorable energetic decrease of amount -e each time a site is осcupied. (a) Find the canonical partition function for N molecules adsorbed on M sites at a temperature T. (b) Find an expression for the chemical potential of an adsorbed molecule, µads- (c) At equilibrium at constant T, show that the dependence of the fraction of occupied sites, x = N/M, is given by the so-called Langmuir adsorption %3D isotherm, cP X = 1+ cP where c is a constant. How does c vary with temperature?
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter6: Forced Convection Over Exterior Surfaces
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6.52P
Related questions
Question
This problem is (16.23) from a book "
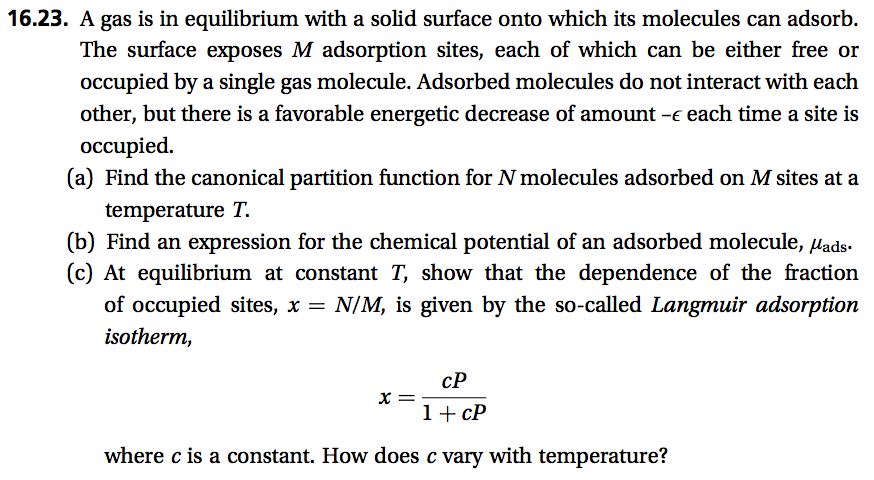
Transcribed Image Text:16.23. A gas is in equilibrium with a solid surface onto which its molecules can adsorb.
The surface exposes M adsorption sites, each of which can be either free or
occupied by a single gas molecule. Adsorbed molecules do not interact with each
other, but there is a favorable energetic decrease of amount -e each time a site is
occupied.
(a) Find the canonical partition function for N molecules adsorbed on M sites at a
temperature T.
(b) Find an expression for the chemical potential of an adsorbed molecule, lads.
(c) At equilibrium at constant T, show that the dependence of the fraction
of occupied sites, x =
isotherm,
N/M, is given by the so-called Langmuir adsorption
cP
1+ cP
where c is a constant. How does c vary with temperature?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning