19.3. (a) Using the chain rule, find ðf/ðz* and df/dz in terms of partial derivatives with respect to x and y. (b) Evaluate d f/əz* and df/ðz assuming that the C-R conditions hold.
19.3. (a) Using the chain rule, find ðf/ðz* and df/dz in terms of partial derivatives with respect to x and y. (b) Evaluate d f/əz* and df/ðz assuming that the C-R conditions hold.
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter5: Rings, Integral Domains, And Fields
Section5.4: Ordered Integral Domains
Problem 8E: If x and y are elements of an ordered integral domain D, prove the following inequalities. a....
Related questions
Question
100%
hi
My question is about Complex Derivative.
I showed in the upload photo.
z is a
f(z)=u(x,y)+i.v(x,y);
In section a, we want to obtain the derivative of the function f with respect to z and z * in the Cartesian
In section b, I want to obtain the derivative of the function f with respect to z and z * in the polar coordinate system.
.
In one of the photos, I put a pattern to solve the question.
Thank you very much.
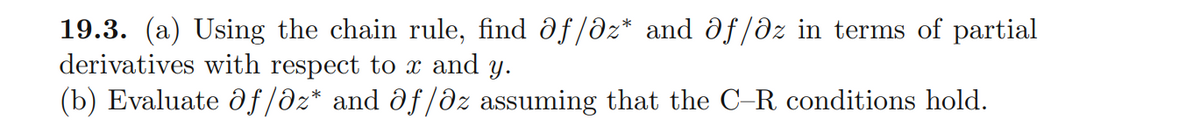
Transcribed Image Text:19.3. (a) Using the chain rule, find ðf/ðz* and df/dz in terms of partial
derivatives with respect to x and y.
(b) Evaluate d f/əz* and df/ðz assuming that the C-R conditions hold.
![For f(z) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y), Definition 19.1.1 yields
df
dz
= lim
Ar-0
u(xo + Ax, yo + Ay) – u(x0, Yo)
Δ+ iΔy
Ay-0
v(xo+Ax, yo + Ay) – v(x0, Yo) ]
Ar + iAy
+i
If this limit is to exist for all paths, it must exist for the two particular paths
on which Ay = 0 (parallel to the a-axis) and Ar = 0 (parallel to the y-axis).
For the first path we get
df
dz
= lim
Ar-0
u(xo+ Ax, yo) – u(xo, yo)
υ (τ0+ Δε, Jo) - υ(ro, Jo)
+i lim
Ar-0
dv
+i
|(x0,y0)
Ax
|(x0.yo)
For the second path (Ax = 0), we obtain
df |
u(xo, Yo + Ay) – u(xo, Yo)
dz
20
= lim
Ay-0
iAy
| n.
|(xo+Y0)
v(xo, Yo + Ay) – v(x0, Yo)
+i lim
Ay-0
iAy
|(x0,Yo)
If f is to be differentiable at zo, the derivatives along the two paths must be
equal. Equating the real and imaginary parts of both sides of this equation
and ignoring the subscript zo (2o, yo, or zo is arbitrary), we obtain
du
dv
du
dv
and
(19.2)
dy
dy
These two conditions, which are necessary for the differentiability of f, are
called the Cauchy–Riemann (C-R) conditions.
The arguments leading to Equation (19.2) imply that the derivative, if it
exists, can be expressed as
in
af
+ i-
(19.3)
dz
fie
||](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F2db0f564-5560-48e1-ad37-7a23e30509ae%2F79738be1-401a-4de8-9eb0-e7d2f7b9f378%2Fcwox7gi_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:For f(z) = u(x, y) + iv(x, y), Definition 19.1.1 yields
df
dz
= lim
Ar-0
u(xo + Ax, yo + Ay) – u(x0, Yo)
Δ+ iΔy
Ay-0
v(xo+Ax, yo + Ay) – v(x0, Yo) ]
Ar + iAy
+i
If this limit is to exist for all paths, it must exist for the two particular paths
on which Ay = 0 (parallel to the a-axis) and Ar = 0 (parallel to the y-axis).
For the first path we get
df
dz
= lim
Ar-0
u(xo+ Ax, yo) – u(xo, yo)
υ (τ0+ Δε, Jo) - υ(ro, Jo)
+i lim
Ar-0
dv
+i
|(x0,y0)
Ax
|(x0.yo)
For the second path (Ax = 0), we obtain
df |
u(xo, Yo + Ay) – u(xo, Yo)
dz
20
= lim
Ay-0
iAy
| n.
|(xo+Y0)
v(xo, Yo + Ay) – v(x0, Yo)
+i lim
Ay-0
iAy
|(x0,Yo)
If f is to be differentiable at zo, the derivatives along the two paths must be
equal. Equating the real and imaginary parts of both sides of this equation
and ignoring the subscript zo (2o, yo, or zo is arbitrary), we obtain
du
dv
du
dv
and
(19.2)
dy
dy
These two conditions, which are necessary for the differentiability of f, are
called the Cauchy–Riemann (C-R) conditions.
The arguments leading to Equation (19.2) imply that the derivative, if it
exists, can be expressed as
in
af
+ i-
(19.3)
dz
fie
||
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage


Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage
