1+9n² b) Determine whether the sequence a, = converges or diverges. If it converges, %3D 1+n find the limit. Please use the attached series test, to correctly solve the problem. *Also when you find the solution, please plug the answer and into this following sentence frame as a conclusion. Sentence Frame: By the is_divergent or convergent 1+9n² 1+n? test, the series a, Show All Your Work! Thank you.
1+9n² b) Determine whether the sequence a, = converges or diverges. If it converges, %3D 1+n find the limit. Please use the attached series test, to correctly solve the problem. *Also when you find the solution, please plug the answer and into this following sentence frame as a conclusion. Sentence Frame: By the is_divergent or convergent 1+9n² 1+n? test, the series a, Show All Your Work! Thank you.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter10: Sequences, Series, And Probability
Section10.3: Geometric Sequences
Problem 49E
Related questions
Question
Hello, complete the attached Calculus question correctly and show all your work. Please use the attached series test, to correctly solve the problem.
*Also when you find the solution, please plug the answer and this following sentence frame as a conclusion.
Sentence Frame: By the ________ test, the series _________ is _divergent or convergent____________.
Thank you.
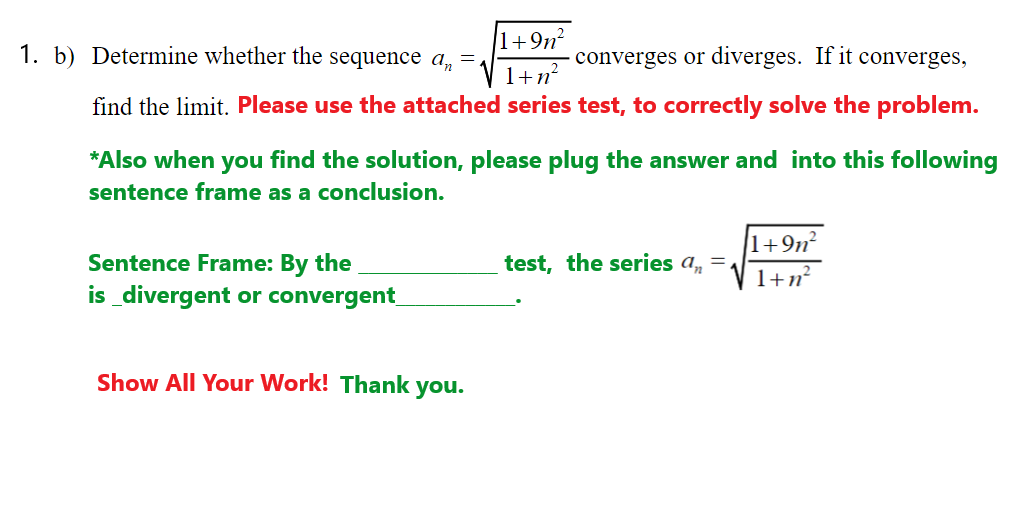
Transcribed Image Text:1. b) Determine whether the sequence a, =.
1+9n²
converges or diverges. If it converges,
1+n²
find the limit. Please use the attached series test, to correctly solve the problem.
*Also when you find the solution, please plug the answer and into this following
sentence frame as
conclusion.
1+9n²
Sentence Frame: By the
test, the series a,
1+n?
is _divergent or convergent
Show All Your Work! Thank you.
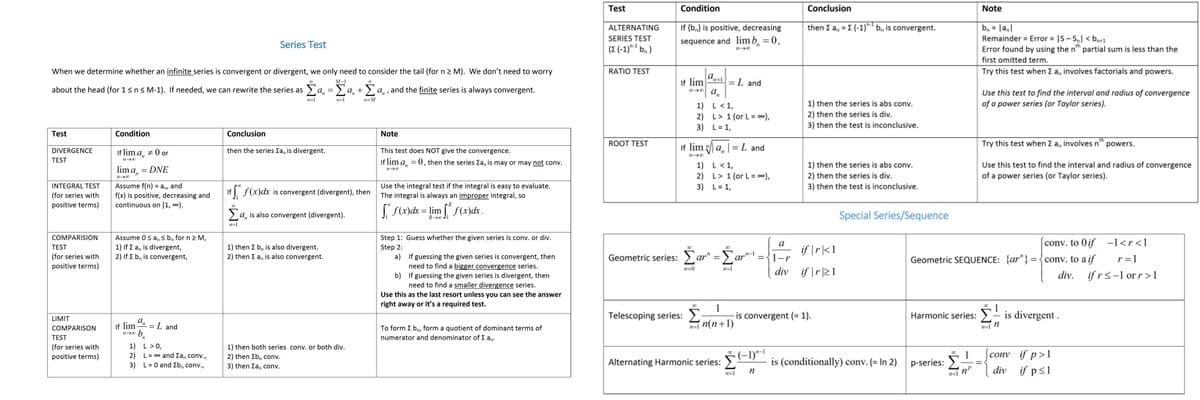
Transcribed Image Text:Test
Condition
Conclusion
Note
If {b,} is positive, decreasing
sequence and lim b, = 0,
then Z a, =E (-1)" b, is convergent.
b, = |anl
Remainder = Error = |S- S,I < bn1
Error found by using the nth partial sum is less than the
first omitted term.
Try this test when Z a, involves factorials and powers.
ALTERNATING
SERIES TEST
Series Test
(E (-1)" b, )
When we determine whether an infinite series is convergent or divergent, we only need to consider the tail (for n2 M). We don't need to worry
RATIO TEST
If lim
n a.
M-1
=L and
about the head (for 1sns M-1). If needed, we can rewrite the series as Ea, =Ea, +Ea, , and the finite series is always convergent.
%3D
Use this test to find the interval and radius of convergence
of a power series (or Taylor series).
1) then the series is abs conv.
1) L<1,
2) L> 1 (or L = 0),
3) L= 1,
2) then the series is div.
3) then the test is inconclusive.
Test
Condition
Conclusion
Note
DIVERGENCE
ROOT TEST
If lim a, |= L and
Try this test when Z a, involves n" powers.
If lim a, +0 or
then the series Za, is divergent.
This test does NOT give the convergence.
TEST
If lim a, = 0, then the series Ea, is may or may not conv.
Use this test to find the interval and radius of convergence
1) L<1,
2) L> 1 (or L= 00),
3) L= 1,
1) then the series is abs conv.
2) then the series is div.
lim a, = DNE
→の
of a power series (or Taylor series).
INTEGRAL TEST
Assume f(n) = an
, and
Use the integral test if the integral is easy to evaluate.
3) then the test is inconclusive.
If, f(x)dx is convergent (divergent), then
(for series with
positive terms)
f(x) is positive, decreasing and
continuous on [1, 0).
The integral is always an improper integral, so
(S(x)dx = lim [" f(x)dx.
a, is also convergent (divergent).
R JI
Special Series/Sequence
n=1
Assume 0s a, s b, for n 2 M,
1) If E a, is divergent,
2) If E b, is convergent,
COMPARISION
Step 1: Guess whether the given series is conv. or div.
a
conv. to 0if -1<r<1
1) then Z b, is also divergent.
2) then Z a, is also convergent.
if |r|<1
TEST
Step 2:
a) If guessing the given series is convergent, then
need to find a bigger convergence series.
Geometric series: ar" =Ear"-
={1-r
(for series with
positive terms)
Geometric SEQUENCE: {ar"} ={conv. to a if
r =1
div if |r|21
n=0
div.
if rs-l or r>1
b) If guessing the given series is divergent, then
need to find a smaller divergence series.
Use this as the last resort unless you can see the answer
right away or it's a required test.
1
-is convergent (= 1).
Harmonic series: >-
1
is divergent .
LIMIT
Telescoping series:
If lim 9
= L and
一→ b
in(n+1)
To form Z b, form a quotient of dominant terms of
numerator and denominator of E an.
COMPARISON
TEST
(for series with
positive terms)
1) L>0,
2) L= 00 and Za, conv.,
1) then both series conv. or both div.
2) then Zb, conv.
1
conv if p>1
Alternating Harmonic series: 5(-1)"
is (conditionally) conv. (= In 2) p-series:
3) L= 0 and Eb, conv.,
3) then Za, conv.
div if p<1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage