2 2 3√2 2. Consider the polar curves C₁ : r = 4 + · cos 0 and C₂:r = 2 − cos as shown in the figure on the right. The curves C₁ and C₂ are both symmetric with respect to the polar axis. Each of these curves is traced counterclockwise as the value of increases on the interval [0, 27]. Also, for each of these curves r > 0 when 0 € [0, 2π]. a. Let P be the point of intersection of C₁ and C₂ in the second quadrant. Find the polar coordinates (r, 0) for the point P where r> 0 when 0 = [0, 2π]. b. Let R be the region that is inside both C₁ and C₂. Set up, but do not evaluate, the integral or sum of integrals for the following: The area of R ● The perimeter of R
2 2 3√2 2. Consider the polar curves C₁ : r = 4 + · cos 0 and C₂:r = 2 − cos as shown in the figure on the right. The curves C₁ and C₂ are both symmetric with respect to the polar axis. Each of these curves is traced counterclockwise as the value of increases on the interval [0, 27]. Also, for each of these curves r > 0 when 0 € [0, 2π]. a. Let P be the point of intersection of C₁ and C₂ in the second quadrant. Find the polar coordinates (r, 0) for the point P where r> 0 when 0 = [0, 2π]. b. Let R be the region that is inside both C₁ and C₂. Set up, but do not evaluate, the integral or sum of integrals for the following: The area of R ● The perimeter of R
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 10DE
Related questions
Question
![2
2
3√2
2. Consider the polar curves C₁ : r = 4 + · cos 0 and C₂:r = 2 − cos as shown in the figure
on the right. The curves C₁ and C₂ are both symmetric with respect to the polar axis. Each of
these curves is traced counterclockwise as the value of increases on the interval [0, 27]. Also,
for each of these curves r > 0 when 0 € [0, 2π].
a. Let P be the point of intersection of C₁ and C₂ in the second quadrant. Find the polar
coordinates (r, 0) for the point P where r> 0 when 0 = [0, 2π].
b. Let R be the region that is inside both C₁ and C₂. Set up, but do not evaluate, the integral or
sum of integrals for the following:
The area of R
●
The perimeter of R](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fd9e35ea0-cf50-41d2-bc0e-945251894e85%2F4045c0d6-f47f-4858-ad09-61a03b13c694%2F4h9zdd6_processed.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:2
2
3√2
2. Consider the polar curves C₁ : r = 4 + · cos 0 and C₂:r = 2 − cos as shown in the figure
on the right. The curves C₁ and C₂ are both symmetric with respect to the polar axis. Each of
these curves is traced counterclockwise as the value of increases on the interval [0, 27]. Also,
for each of these curves r > 0 when 0 € [0, 2π].
a. Let P be the point of intersection of C₁ and C₂ in the second quadrant. Find the polar
coordinates (r, 0) for the point P where r> 0 when 0 = [0, 2π].
b. Let R be the region that is inside both C₁ and C₂. Set up, but do not evaluate, the integral or
sum of integrals for the following:
The area of R
●
The perimeter of R
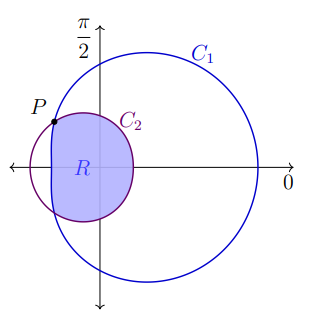
Transcribed Image Text:P
π
2
R
C₂
C₁
0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage