2- An inverted pendulum with a constant rod length of (r) is mechanically fixed to a floor via a DC motor at point P (0,0); see Fig. 4. A flywheel with a mass of (m) and inertia of (1) is attached to the pendulum tip. The motor can generate rotational motion along the a axis, and its output torque is symbolized with (r). The gear and bearings introduce torsional viscous dissipation with a damping coefficient of c. Gravitational acceleration is 9.81 m/s². A torsional spring with a stiffness constant of (k) acts along the a axis. The spring is in rest condition when a = O radians. J = K1/50 = kgm² m = K3 = kg r= K2/4 = c= (K2+K3) / 10 = -. Nms/rad k(spring) = K1*15= Nm/rad Note that K1, K2 and K3 are from Question 0. a=0 m k Fig. 4: An inverted pendulum with o flywheel at the tip. Obtain the mathematical model of the system. You should use the numeric values for the system parameters (m, J, c, b, k). If you leave them symbolic, your answer will be given a score of 0. 3- Linearize the mathematical model provided in Question 2 using the following: sin a = a cos a = 1 Obtain the time response of a(t), by solving the mathematical model after linearization. In that case, the torque input and initial values are given as follows: 1 = Step Input with an amplitude of – 5 Nm a, = 0.1 radians (initial angle) rad å, = 0.2 (initial angular velocity) of
2- An inverted pendulum with a constant rod length of (r) is mechanically fixed to a floor via a DC motor at point P (0,0); see Fig. 4. A flywheel with a mass of (m) and inertia of (1) is attached to the pendulum tip. The motor can generate rotational motion along the a axis, and its output torque is symbolized with (r). The gear and bearings introduce torsional viscous dissipation with a damping coefficient of c. Gravitational acceleration is 9.81 m/s². A torsional spring with a stiffness constant of (k) acts along the a axis. The spring is in rest condition when a = O radians. J = K1/50 = kgm² m = K3 = kg r= K2/4 = c= (K2+K3) / 10 = -. Nms/rad k(spring) = K1*15= Nm/rad Note that K1, K2 and K3 are from Question 0. a=0 m k Fig. 4: An inverted pendulum with o flywheel at the tip. Obtain the mathematical model of the system. You should use the numeric values for the system parameters (m, J, c, b, k). If you leave them symbolic, your answer will be given a score of 0. 3- Linearize the mathematical model provided in Question 2 using the following: sin a = a cos a = 1 Obtain the time response of a(t), by solving the mathematical model after linearization. In that case, the torque input and initial values are given as follows: 1 = Step Input with an amplitude of – 5 Nm a, = 0.1 radians (initial angle) rad å, = 0.2 (initial angular velocity) of
Related questions
Question
Please help asap :))))) Just use the question 2 as a mathematical model solve question 3 please. You don't need to solve question 2. Take K1= 1, K2=8, K3=3,K4=4
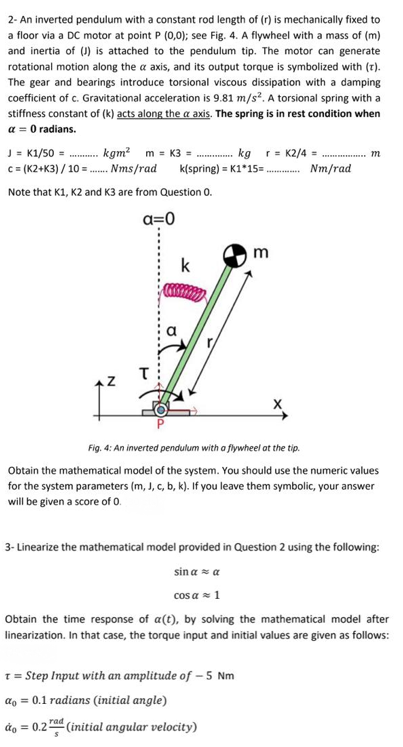
Transcribed Image Text:2- An inverted pendulum with a constant rod length of (r) is mechanically fixed to
a floor via a DC motor at point P (0,0); see Fig. 4. A flywheel with a mass of (m)
and inertia of (1) is attached to the pendulum tip. The motor can generate
rotational motion along the a axis, and its output torque is symbolized with (r).
The gear and bearings introduce torsional viscous dissipation with a damping
coefficient of c. Gravitational acceleration is 9.81 m/s². A torsional spring with a
stiffness constant of (k) acts along the a axis. The spring is in rest condition when
a = 0 radians.
J = K1/50 = .. kgm? m = K3 =
c (K2+K3) / 10 = . Nms/rad k(spring) = K1*15= . Nm/rad
..... kg r= K2/4 = .
Note that K1, K2 and K3 are from Question 0.
a=0
m
k
Fig. 4: An inverted pendulum with a flywheel ot the tip.
Obtain the mathematical model of the system. You should use the numeric values
for the system parameters (m, J, c, b, k). If you leave them symbolic, your answer
will be given a score of 0.
3- Linearize the mathematical model provided in Question 2 using the following:
sin a = a
cos a = 1
Obtain the time response of a(t), by solving the mathematical model after
linearization. In that case, the torque input and initial values are given as follows:
1= Step Input with an amplitude of – 5 Nm
a, = 0.1 radians (initial angle)
rad
áo = 0.2 (initial angular velocity)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images
