2) Consider the initial boundary value problems: Ofu – azu = 0, u(п, 0) — 0, u(0, t) = 0, x E (0, 1), t > 0, дди (х, 0) — 1, u(T, t) = 0, x E (0, 7), initial data, t > 0, boundary values. (a) Solve it using formula (1). (b) Is the resulting solution continuous? Is C1 i.e, u(x, t) differentiable th ôu(x, t), Ôgu(x,t) continuous?
2) Consider the initial boundary value problems: Ofu – azu = 0, u(п, 0) — 0, u(0, t) = 0, x E (0, 1), t > 0, дди (х, 0) — 1, u(T, t) = 0, x E (0, 7), initial data, t > 0, boundary values. (a) Solve it using formula (1). (b) Is the resulting solution continuous? Is C1 i.e, u(x, t) differentiable th ôu(x, t), Ôgu(x,t) continuous?
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter6: Matrices And Determinants
Section6.4: Determinants And Cramer’s Rule
Problem 3E
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:(1)
u(r +h, t+ k) + u(x – h, t – k) = u(x+ k,t+ h) + u(x – k, t – h),
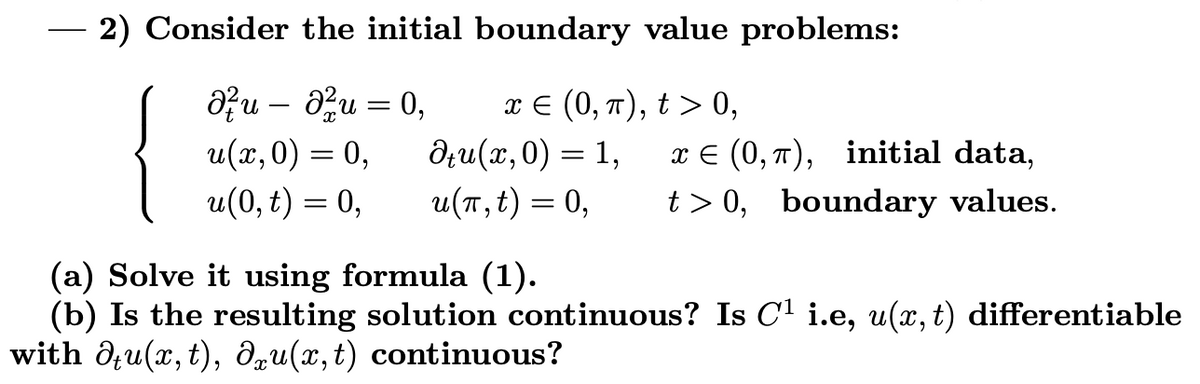
Transcribed Image Text:2) Consider the initial boundary value problems:
{
Ə?u – au = 0,
u(х, 0) — 0,
u(0, t) = 0,
πε (0, π ) ,t> 0,
дли (и, 0) — 1,
u(T, t) = 0,
6.
x E (0, 7), initial data,
t > 0, boundary values.
%3D
(a) Solve it using formula (1).
(b) Is the resulting solution continuous? Is C1 i.e, u(, t) differentiable
with d;u(x, t), dqu(x,t) continuous?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning