2. Below is the structure of an anti-inflammatory drug: F == Ο NH2 F N. N CH₂ A) How many rings are able to undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution (EARS)? ( B) Which of the rings is/are ACTIVATED for EARS? Encircle it/them on the structure. C) For each ring in B, answer the following statement: "The ring is activated because its substituent is (A. electron-donating; B. electron- withdrawing) through (A. inductive; B. resonance) effects. D) Which of the rings is/are DEACTIVATED for EARS? Box it/them on the structure. E) For each ring in D, answer the following statement: "The ring is deactivated because its substituent is (A. electron-donating; B. electron-withdrawing) through (A. inductive; B. resonance) effects. F) Draw the structure of a plausible product when this compound undergoes monobromination.
2. Below is the structure of an anti-inflammatory drug: F == Ο NH2 F N. N CH₂ A) How many rings are able to undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution (EARS)? ( B) Which of the rings is/are ACTIVATED for EARS? Encircle it/them on the structure. C) For each ring in B, answer the following statement: "The ring is activated because its substituent is (A. electron-donating; B. electron- withdrawing) through (A. inductive; B. resonance) effects. D) Which of the rings is/are DEACTIVATED for EARS? Box it/them on the structure. E) For each ring in D, answer the following statement: "The ring is deactivated because its substituent is (A. electron-donating; B. electron-withdrawing) through (A. inductive; B. resonance) effects. F) Draw the structure of a plausible product when this compound undergoes monobromination.
Related questions
Question
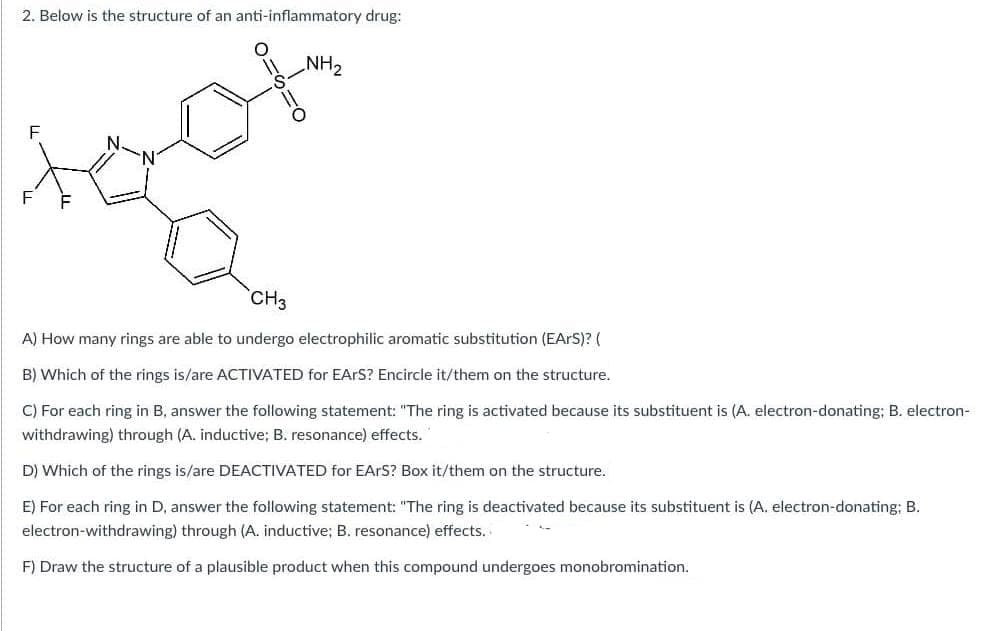
Transcribed Image Text:2. Below is the structure of an anti-inflammatory drug:
F
==
Ο
NH2
F
N.
N
CH₂
A) How many rings are able to undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution (EARS)? (
B) Which of the rings is/are ACTIVATED for EARS? Encircle it/them on the structure.
C) For each ring in B, answer the following statement: "The ring is activated because its substituent is (A. electron-donating; B. electron-
withdrawing) through (A. inductive; B. resonance) effects.
D) Which of the rings is/are DEACTIVATED for EARS? Box it/them on the structure.
E) For each ring in D, answer the following statement: "The ring is deactivated because its substituent is (A. electron-donating; B.
electron-withdrawing) through (A. inductive; B. resonance) effects.
F) Draw the structure of a plausible product when this compound undergoes monobromination.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images
