2. Consider a trader with initial fund given by To = 15, and the transaction cost function of holding q shares of stock i is C(g) = 10 + q*. The price (r.) at which this trader sells its position is stochastically distributed according to the following probability distribution: P(z,) = {0.5, if z, = 88 10.5, if z, = $2 Let a random variable i be the profit of trading at each time t, t = 1,2,...,T, (a) If the trader's utility function is given by u(#) = u(#) – 0(#), %3D
2. Consider a trader with initial fund given by To = 15, and the transaction cost function of holding q shares of stock i is C(g) = 10 + q*. The price (r.) at which this trader sells its position is stochastically distributed according to the following probability distribution: P(z,) = {0.5, if z, = 88 10.5, if z, = $2 Let a random variable i be the profit of trading at each time t, t = 1,2,...,T, (a) If the trader's utility function is given by u(#) = u(#) – 0(#), %3D
College Algebra
7th Edition
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Chapter9: Counting And Probability
Section9.4: Expected Value
Problem 1E: If a game gives payoffs of $10 and $100 with probabilities 0.9 and 0.1, respectively, then the...
Related questions
Question
Hello, Could I have help with this question? It is a HW assignment and not graded.
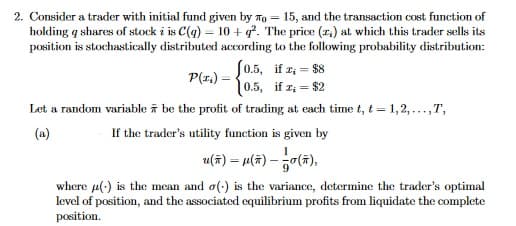
Transcribed Image Text:2. Consider a trader with initial fund given by To = 15, and the transaction cost function of
holding q shares of stock i is C(g) = 10 + q. The price (r.) at which this trader sells its
position is stochastically distributed according to the following probability distribution:
P(z,) = 0.5, if z, = $8
10.5, if z; = $2
Let a random variable ī be the profit of trading at each time t, t = 1,2, ...,T,
(a)
If the trader's utility function is given by
u(주) -M(#) - 능0(㈜),
where u(-) is the mean and o(:) is the variance, determine the trader's optimal
level of position, and the associated equilibrium profits from liquidate the complete
position.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning