2. Hemoglobin releases protons upon oxygen binding. This phenomenon is called the Bohr effect, and an important group that participates is histidine 146 of the B subunit. In deoxyhemoglobin histidine 146 forms a salt bridge with aspartic acid 94. CH 'N. C-O- *HN `CH, The salt bridge is disrupted upon oxygenation: deoxyhemoglobin oxyhemoglobin his146 asp94 asp94 his146 The pKa of the histidine side group in the deoxy form is higher than that in the free amino acid, but changes upon oxygenation of the heme Fe(II) atom. How does the pKạ change (i.e., Bi214 Lab 3 Report 1 does it increase or decrease)? Why does this change occur?
2. Hemoglobin releases protons upon oxygen binding. This phenomenon is called the Bohr effect, and an important group that participates is histidine 146 of the B subunit. In deoxyhemoglobin histidine 146 forms a salt bridge with aspartic acid 94. CH 'N. C-O- *HN `CH, The salt bridge is disrupted upon oxygenation: deoxyhemoglobin oxyhemoglobin his146 asp94 asp94 his146 The pKa of the histidine side group in the deoxy form is higher than that in the free amino acid, but changes upon oxygenation of the heme Fe(II) atom. How does the pKạ change (i.e., Bi214 Lab 3 Report 1 does it increase or decrease)? Why does this change occur?
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Chapter7: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 7TYK
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
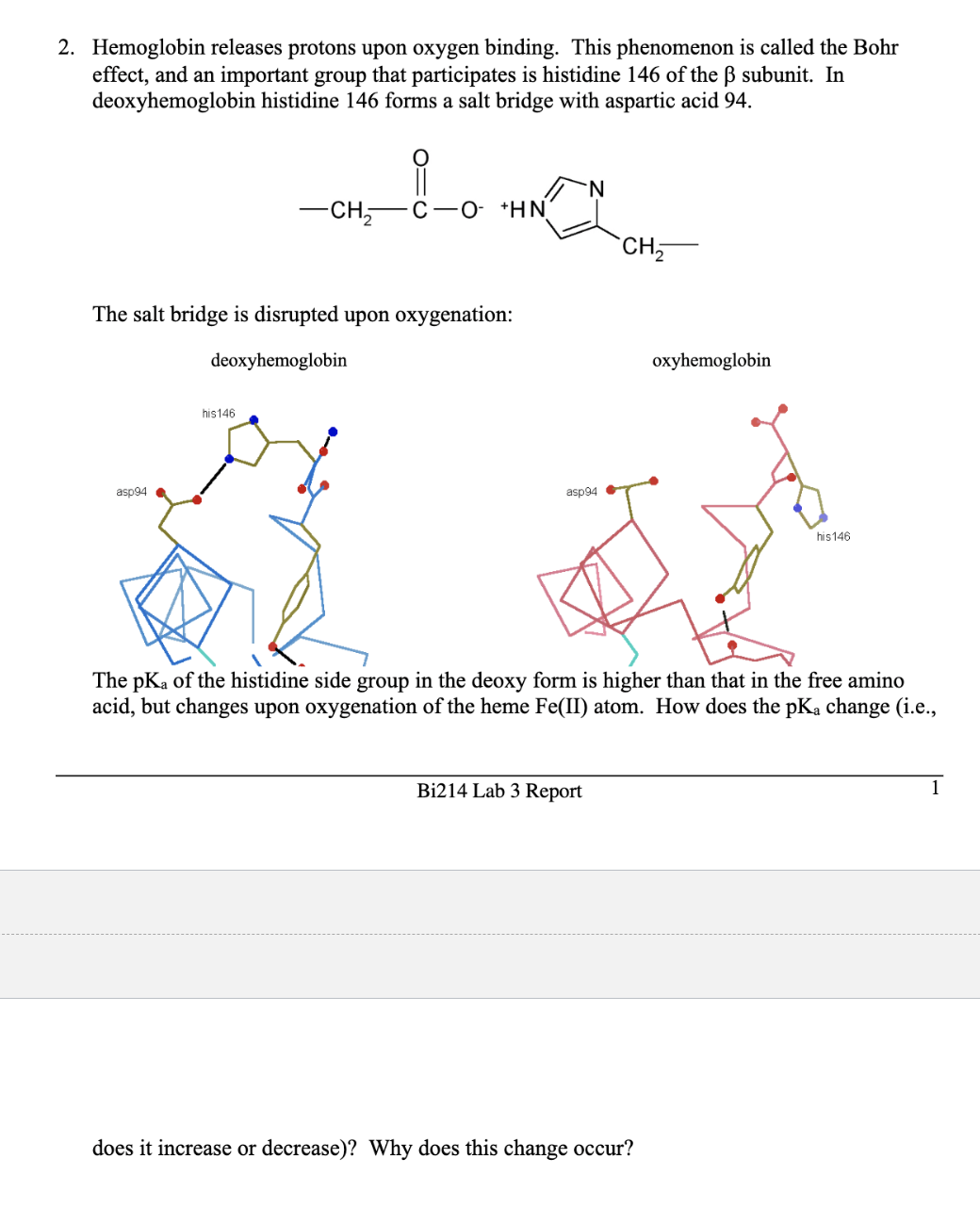
Transcribed Image Text:2. Hemoglobin releases protons upon oxygen binding. This phenomenon is called the Bohr
effect, and an important group that participates is histidine 146 of the B subunit. In
deoxyhemoglobin histidine 146 forms a salt bridge with aspartic acid 94.
CH
'N.
C-O- *HN
`CH,
The salt bridge is disrupted upon oxygenation:
deoxyhemoglobin
oxyhemoglobin
his146
asp94
asp94
his146
The pKa of the histidine side group in the deoxy form is higher than that in the free amino
acid, but changes upon oxygenation of the heme Fe(II) atom. How does the pKạ change (i.e.,
Bi214 Lab 3 Report
1
does it increase or decrease)? Why does this change occur?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:
9781305389892
Author:
Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap…
Biology
ISBN:
9781305073951
Author:
Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:
Cengage Learning