2. Let V be the set of all real numbers with the two operations and defined by u v=u+v- 2 and ku = ku+ (1+ k) (a) Compute 201 Solution : 201 = (b) Compute 083 Solution : 083 = (c) Verify Ariom 4: Solution : We have u ) = role of %3! %3D = u for every u = u in V; thus the nu: the zero vector in V; so 0 = (d) Verify Axiom 5: Solution : For each u = u in V, we have %3D 0: thus the number
2. Let V be the set of all real numbers with the two operations and defined by u v=u+v- 2 and ku = ku+ (1+ k) (a) Compute 201 Solution : 201 = (b) Compute 083 Solution : 083 = (c) Verify Ariom 4: Solution : We have u ) = role of %3! %3D = u for every u = u in V; thus the nu: the zero vector in V; so 0 = (d) Verify Axiom 5: Solution : For each u = u in V, we have %3D 0: thus the number
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.4: Applications
Problem 32EQ
Related questions
Question
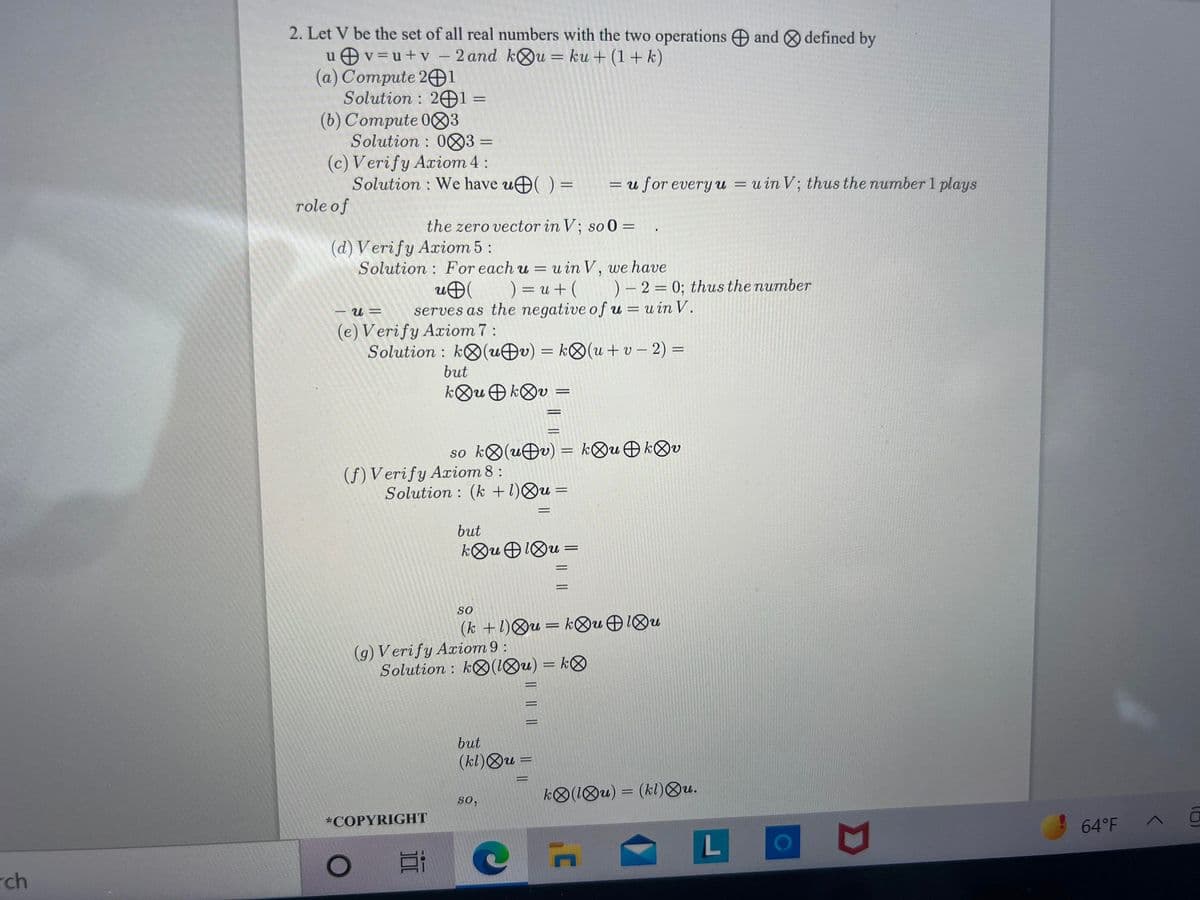
Transcribed Image Text:2. Let V be the set of all real numbers with the two operations and defined by
u Ov=u+v – 2 and kOu = ku + (1+ k)
(a) Compute 201
Solution : 2Ð1 =
(b) Compute 083
Solution : 083 =
(c) Verify Axiom 4:
Solution : We have u( ) =
%3D
= u for every u = uin V; thus the number 1 plays
role of
the zero vector in V; so 0 =
(d) V erify Axiom 5:
Solution : For each u = u in V, we have
uÐ
serves as the negative of u = u in V.
) = u + ( )– 2 = 0; thus the number
%3D
(e) Verify Axiom 7 :
Solution : kO(uÐv) = k®(u+ v – 2) =
but
kOu O kOv
so ko(uÐv) = k®uOkOv
(f) Verify Axiom 8 :
Solution : (k +1)Ou =
%3D
but
so
(k +1)Qu= k&u 1Ou
(g) Verify Axiom 9 :
Solution : kO(1Ou) = k®
%3D
%3D
%3D
but
(kl)Ou =
k®(1Ou) = (kl)®u.
%3D
so,
*COPYRIGHT
64°F A
rch
IL || ||
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,