2. Show that the scalar product of two vectors remains invariant at linear transformations of the vectors if and only if the transformations are orthogonal. That is, given two vectors a; and bi, and a simultaneous linear transformation ai + ái = Rijaj bi → bį = Rijbj (5) show that we have aźb; = a;b; if an only if the matrix R is orthogonal. The Einstein summation convention is implied throughout. Hint: If you have more than one implicit summation in the same formula, make sure to prop- erly differentiate between the summations by denoting the corresponding summation indices with different letters! In other words, an index cannot be repeated more than once in any given formula.
2. Show that the scalar product of two vectors remains invariant at linear transformations of the vectors if and only if the transformations are orthogonal. That is, given two vectors a; and bi, and a simultaneous linear transformation ai + ái = Rijaj bi → bį = Rijbj (5) show that we have aźb; = a;b; if an only if the matrix R is orthogonal. The Einstein summation convention is implied throughout. Hint: If you have more than one implicit summation in the same formula, make sure to prop- erly differentiate between the summations by denoting the corresponding summation indices with different letters! In other words, an index cannot be repeated more than once in any given formula.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter7: Distance And Approximation
Section7.4: The Singular Value Decomposition
Problem 27EQ
Related questions
Question
Please provide neat and clean handwriting
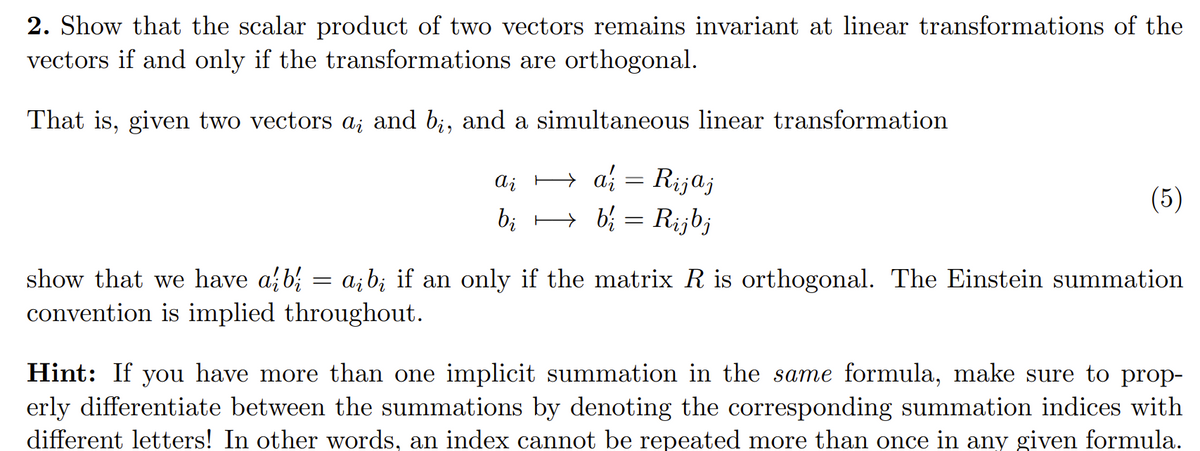
Transcribed Image Text:2. Show that the scalar product of two vectors remains invariant at linear transformations of the
vectors if and only if the transformations are orthogonal.
That is, given two vectors a; and bį, and a simultaneous linear transformation
ai = Rijaj
bib₁ = Rijbj
Ai
(5)
=
show that we have a bi ai bį if an only if the matrix R is orthogonal. The Einstein summation
convention is implied throughout.
Hint: If you have more than one implicit summation in the same formula, make sure to prop-
erly differentiate between the summations by denoting the corresponding summation indices with
different letters! In other words, an index cannot be repeated more than once in any given formula.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,