2. The lateral or transverse magnification of an image is the one we've been using, a ratio of the height of the image to that of the object: M7 = L = -. The angular magnification is the ratio of the angle subtended by the image to that subtended by the object: mg =%. There is one other form of magnification that may be of interest, the longitudinal magnification, which is the ratio of the “width" of the image along the optical axis to the "width" of the object: M1 = 4, as shown below L L' object image (a) f. From the thin lens/mirror equation, calculate ds' /ds for fixed focal length (a) Show that if L and L'are small compared to their distances from the (b) lens/mırror (i.e., L z ds and L' z ds'), the longitudinal magnification can be written in terms of the lateral magnification:
2. The lateral or transverse magnification of an image is the one we've been using, a ratio of the height of the image to that of the object: M7 = L = -. The angular magnification is the ratio of the angle subtended by the image to that subtended by the object: mg =%. There is one other form of magnification that may be of interest, the longitudinal magnification, which is the ratio of the “width" of the image along the optical axis to the "width" of the object: M1 = 4, as shown below L L' object image (a) f. From the thin lens/mirror equation, calculate ds' /ds for fixed focal length (a) Show that if L and L'are small compared to their distances from the (b) lens/mırror (i.e., L z ds and L' z ds'), the longitudinal magnification can be written in terms of the lateral magnification:
Related questions
Question
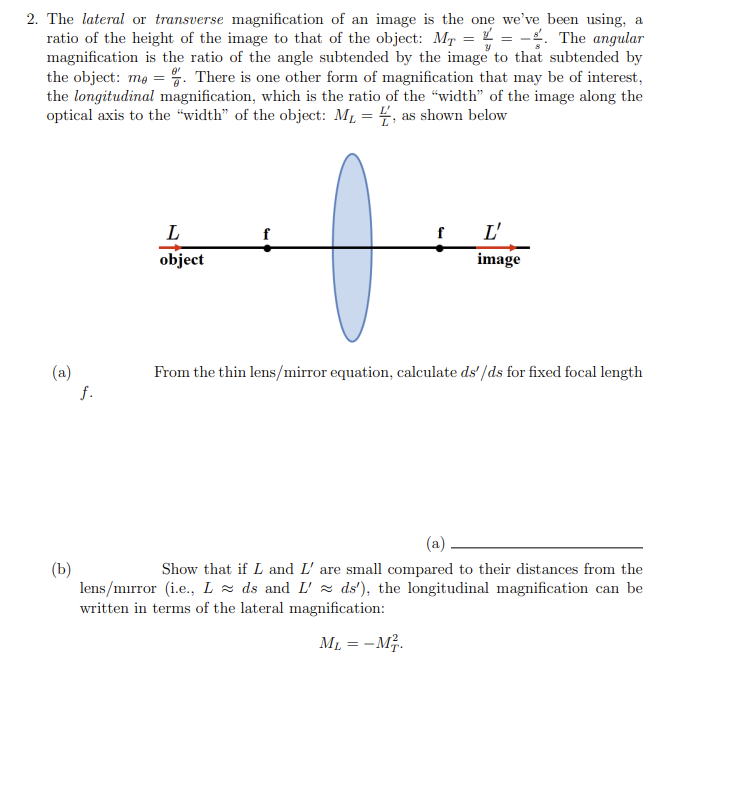
Transcribed Image Text:2. The lateral or transverse magnification of an image is the one we've been using, a
ratio of the height of the image to that of the object: MT = L = -. The angular
magnification is the ratio of the angle subtended by the image to that subtended by
the object: mg =%. There is one other form of magnification that may be of interest,
the longitudinal magnification, which is the ratio of the “width" of the image along the
optical axis to the “width" of the object: M1 = 4, as shown below
L
f L'
object
image
(a)
f.
From the thin lens/mirror equation, calculate ds' /ds for fixed focal length
(a)
(b)
lens/mırror (i.e., L - ds and L' ds'), the longitudinal magnification can be
written in terms of the lateral magnification:
Show that if L and L' are small compared to their distances from the
ML = –M.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images
