Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.4: Applications
Problem 2EQ: 2. Suppose that in Example 2.27, 400 units of food A, 500 units of B, and 600 units of C are placed...
Related questions
Question
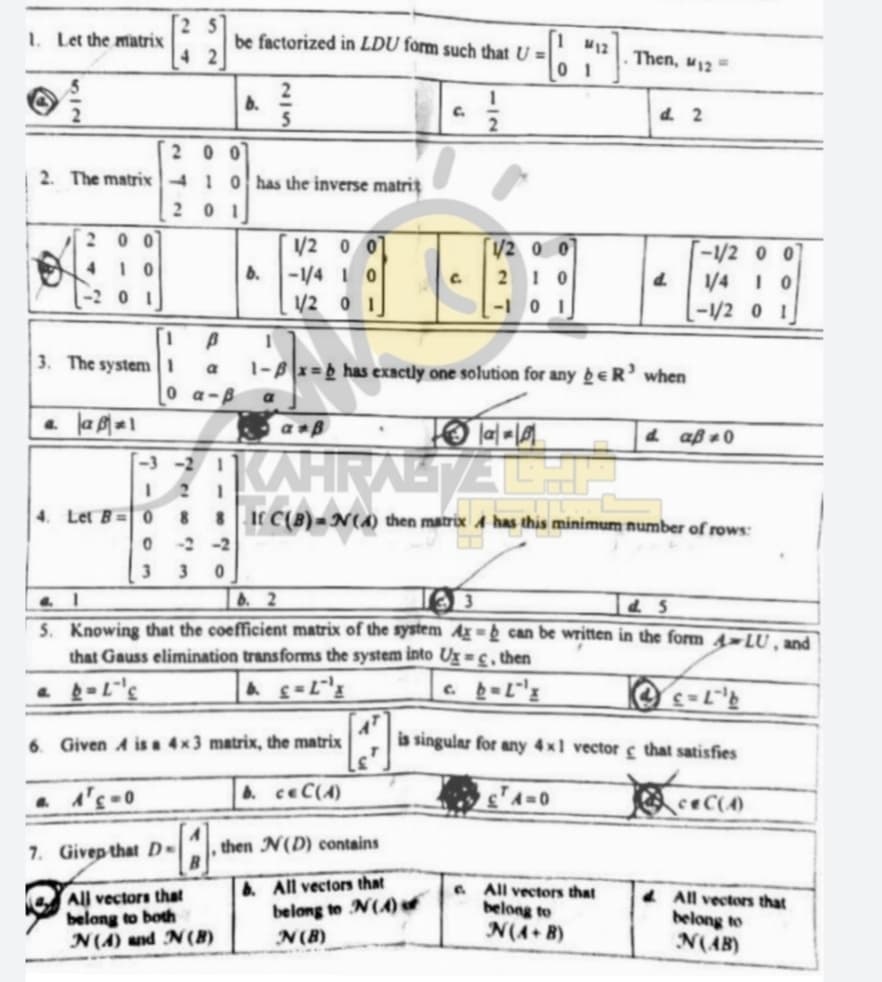
Transcribed Image Text:1. Let the matrix
42
be factorized in LDU form such that U =
12
Then, M12
0 1
6.
C.
d. 2
2 0 0
2. The matrix41 0has the inverse matrit
20 1
200
/2 0 0
/2 0 0
-1/2 0 0
1/4 I 0
-1/2 0 1
4.
-/4 10
/2 0 1
C.
2 1 0
-2 01
-I 0 1
1.
3. The system1
1-8x=b has exactly one solution for any be R' when
a
0 a-B
a *B
d aß 0
KAHRABTE
-3 -2 1
4. Let B= 0
8 8I C(B) =N(A) then matrix A has this minimum number of rows:
0 2 -2
3 3 0
6. 2
3. Knowing that the coefficient matrix of the system d= can be written in the form 4-LU, and
that Gauss elimination transforms the system into Ug =c, then
6. Given A is a 4x3 matrix, the matrix
is singular for any 4x1 vector s that satisfies
A ceC(A)
ceC(4)
7. Givep that D-
then N(D) contains
All vectors that
belang to both
N(A) and N(8)
& All vectors that
belong to N(A)
N(B)
. All vectors that
belong to
N(A+ B)
4 All vectors that
belong to
N(AB)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage