3-48 Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown in Fig. P3-48. If the specific gravity of ene fluid is 1355, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolute pressare of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 100 kPa Arswer. 5.0 Air SG 22 cm SG, - 1355 FIGURE P3-48
3-48 Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air pipe shown in Fig. P3-48. If the specific gravity of ene fluid is 1355, determine the specific gravity of the other fluid for the indicated absolute pressare of air. Take the atmospheric pressure to be 100 kPa Arswer. 5.0 Air SG 22 cm SG, - 1355 FIGURE P3-48
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Chapter1: Introduction
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P
Related questions
Question
i need the answer quickly
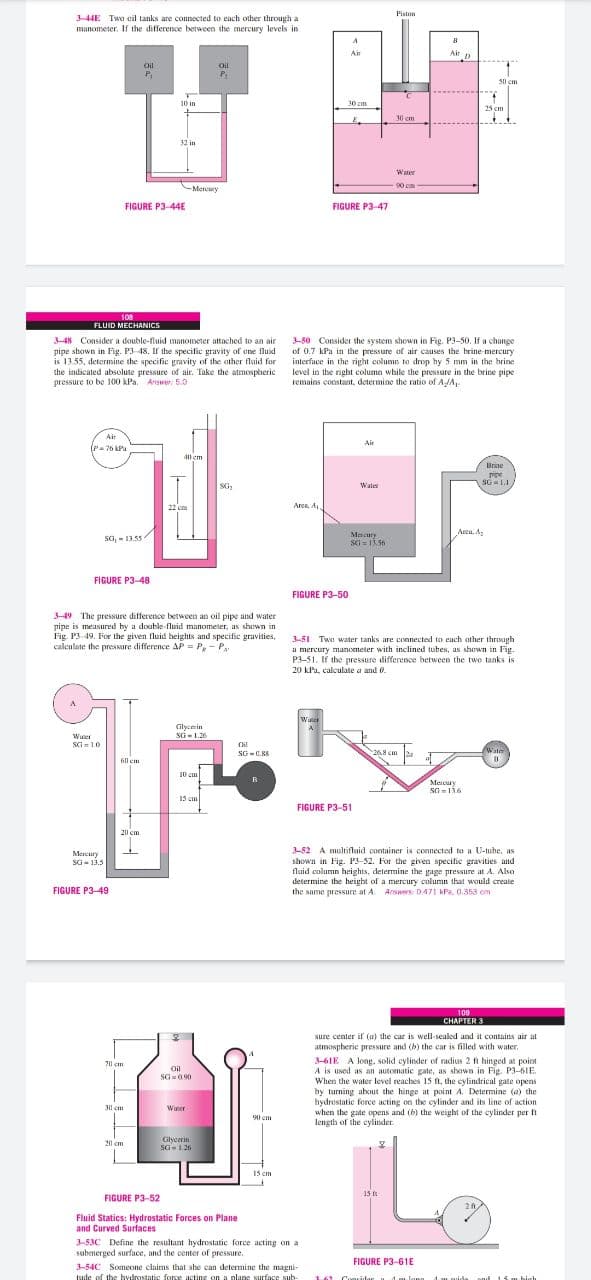
Transcribed Image Text:Piston
344E Twa eil tanks are connected to each other through a
manometer. If the difference between the mercury levels in
Air
Air a
Oil
Oil
50 em
10 in
30 cm
25 cm
30 cm
32 in
Water
90 cm
-Mereury
FIGURE P3-44E
FIGURE P3-47
108
FLUID MECHANICS
3-48 Consider a double-fluid manometer attached to an air
pipe shown in Fig. P3 48. If the specific gravity of ene fluid
is 13.55, determine the specific pgravity of the other fluid for
the indicated absolute pressure of air. Take the atmospheric
pressure to be 100 kPa. Answer: 5.0
3-50 Consider the system shown in Fig. P3-50, If a change
of 0.7 kPa in the pressure of air causes the brine mercury
interface in the right column to drop hy 5 mm in the brine
level in the right column while the pressure in the brine pipe
remains constant, determine the ratio of AJA
Air
Air
(P=76 kPa
40 cm
Brne
pipe
SG-1.1
Wates
Area A
22 cm
Area, A,
SG, - 13.55
Mncury
SG = 11 56
FIGURE P3-48
FIGURE P3-50
3-49 The pressure difference between an oil pipe and water
pipe is measured by a double-fluid manometer, as shwn in
Fig. P3 49. For the given fluid heights and specific gravities,
calculate the pressure difference AP = P - P,
3-51 Twi water tanks are connected to each ather through
a mercury manometer with inclined tubes, as shown in Fig.
P3-51. If the pressure difference between the two tanks is
20 kPa, calculate a and o.
Water
Glycerin
scie 1
Water
SG-1.26
SG=10
Oil
SG -C.88
26 cm 2a
60 em
10 cm
Mercury
SG - 136
15 cm
FIGURE P3-51
20 cm
3-52 A multifluid container is connected to a U-tuhe, as
Mercury
SG - 13.5
shown in Fig. P3-52. For the given specific gravities and
fluid column heights, determine the gage pressure at A. Alsa
determine the height of a mercury column that would create
the same pressure at A. Answs DA71 KPa, 0.353 om
FIGURE P3-49
109
CHAPTER 3
sure center if (a) the car is well-sealed and it contains air at
atmospherie pressure and (b) the car is filled with water,
3-61E A long, solid cylinder of radius 2 ft hinged at point
A is used as an automatic gate, as shown in Fig. P3-61E.
When the water level reaches 15 fi, the cylindrical gate opens
by turning about the hinge at point A. Determine (a) the
hydrestatic force acting on the cylinder and its line of action
when the gate opens and (b) the weight of the cylinder per ft
length of the cylinder
70 cm
Oil
SG=090
30 cm
Waner
90 cm
Glycerin
SG- 1.26
20 cm
15 cm
15 t
FIGURE P3-52
Fluid Statics: Hydrostatic Forces on Plane
and Curved Surfaces
3-53C Define the resultant hydrostatic force acting on a
submerged surface, and the center of pressure.
FIGURE P3-61E
3-54C Someone claims that she can determine the magni
tude of the hydrostatie forge acting on a plane surface sut
6 Co
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781259696527
Author:
J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed…
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780133887518
Author:
H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:
Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285061238
Author:
Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:
Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:
9780072848236
Author:
Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Companies, The