3 Let U2 = -3 Uz be a basis for IR³. Use the Gram-Schmidt process to find an orthogonal basis under the Euclidean inner product. Orthogonal basis: { V1 > V2 = V3 a = Ex: 5 = Ex: 5 C = Ex: 5
3 Let U2 = -3 Uz be a basis for IR³. Use the Gram-Schmidt process to find an orthogonal basis under the Euclidean inner product. Orthogonal basis: { V1 > V2 = V3 a = Ex: 5 = Ex: 5 C = Ex: 5
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.6: The Matrix Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 38EQ
Related questions
Question
100%
Can I get help with this "finding an orthogonal basis using the Gram-Schmidt process" problem?
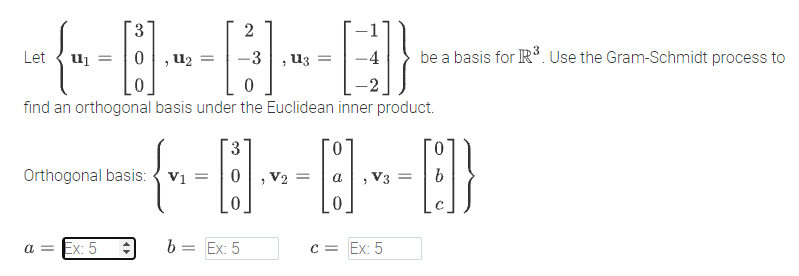
Transcribed Image Text:3
Let
U2 =
-3
Uz
be a basis for IR³. Use the Gram-Schmidt process to
find an orthogonal basis under the Euclidean inner product.
Orthogonal basis: { V1
> V2 =
V3
a = Ex: 5
= Ex: 5
C = Ex: 5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage