(3) Proving that sin?(x) + cos (x) = 1: d. (a) Show that -(cos² (x)+ sin (x)) = 0. What does the constant function theorem d.x tell you about sin?(x) + cos²(x)?
(3) Proving that sin?(x) + cos (x) = 1: d. (a) Show that -(cos² (x)+ sin (x)) = 0. What does the constant function theorem d.x tell you about sin?(x) + cos²(x)?
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.4: Multiple-angle Formulas
Problem 41E
Related questions
Question
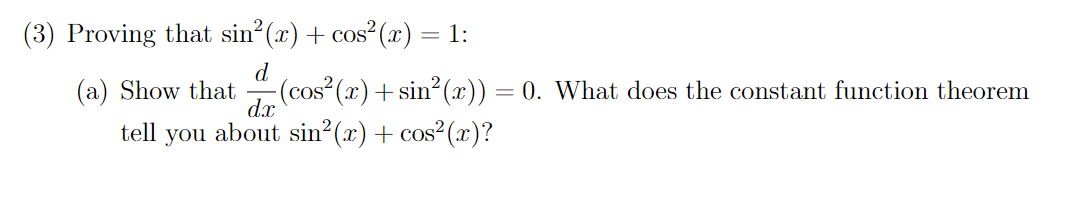
Transcribed Image Text:(3) Proving that sin?(x) + cos (x) = 1:
d.
(a) Show that
-(cos² (x)+ sin (x)) = 0. What does the constant function theorem
d.x
tell
you
about sin?(x) + cos²(x)?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage