3) What is V(c) - V(a), the potentital difference between the outer surface of the conductor and the outer surface of the insulator? V Submit
3) What is V(c) - V(a), the potentital difference between the outer surface of the conductor and the outer surface of the insulator? V Submit
Related questions
Question
Only need Q3
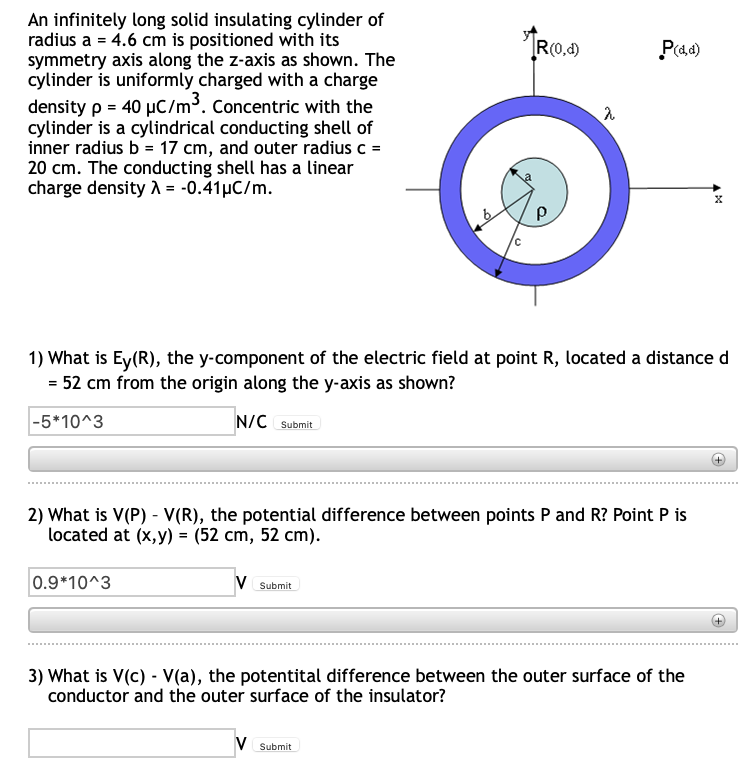
Transcribed Image Text:An infinitely long solid insulating cylinder of
radius a = 4.6 cm is positioned with its
symmetry axis along the z-axis as shown. The
cylinder is uniformly charged with a charge
density p = 40 µC/m³. Concentric with the
cylinder is a cylindrical conducting shell of
inner radius b = 17 cm, and outer radius c =
20 cm. The conducting shell has a linear
charge density A = -0.41µC/m.
R(0,d)
P(aa)
1) What is Ey(R), the y-component of the electric field at point R, located a distance d
= 52 cm from the origin along the y-axis as shown?
|-5*10^3
N/C Submit
2) What is V(P) - V(R), the potential difference between points P and R? Point P is
located at (x,y) = (52 cm, 52 cm).
0.9*10^3
V Submit
3) What is V(c) - V(a), the potentital difference between the outer surface of the
conductor and the outer surface of the insulator?
V Submit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps
