3. Consider the vectors 1 W1 E W2 = and the subspace W = span{w₁, W2, W3} CR¹. (a) Find an orthogonal basis for W. W3 = 0
3. Consider the vectors 1 W1 E W2 = and the subspace W = span{w₁, W2, W3} CR¹. (a) Find an orthogonal basis for W. W3 = 0
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.6: The Matrix Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 38EQ
Related questions
Question
Solve first four parts
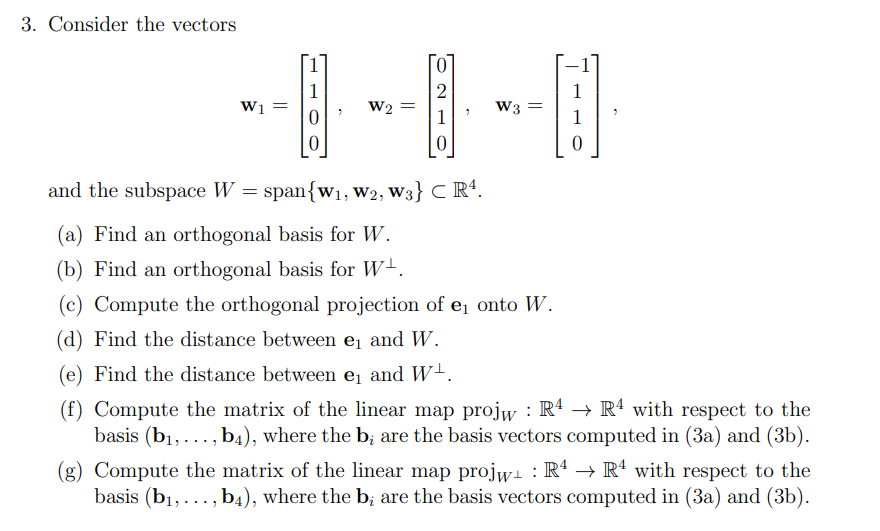
Transcribed Image Text:3. Consider the vectors
1
W1
O |H|
W2 =
0
and the subspace W = span{w₁, W2, W3} CR¹.
(a) Find an orthogonal basis for W.
(b) Find an orthogonal basis for W¹.
(c) Compute the orthogonal projection of e₁ onto W.
(d) Find the distance between ₁ and W.
(e) Find the distance between e₁ and W-.
(f) Compute the matrix of the linear map projw: R4 → R4 with respect to the
basis (b₁,..., b4), where the b; are the basis vectors computed in (3a) and (3b).
(g) Compute the matrix of the linear map projw₁ : R4 → R4 with respect to the
basis (b₁,..., b4), where the b; are the basis vectors computed in (3a) and (3b).
W3 =
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning