30. Velocity of a Star The space velocity v of a star relative to the sun can be expressed as the resultant vector of two perpendicular vectors-the radial velocity v, and the tangential velocity v,, where v = v, + v,. If a star is located near the sun and its space velocity is large, then its motion across the sky will also be large. Barnard's Star is a relatively close star with a distance of 35 trillion mi from the sun. It Barnard's Star Sun moves across the sky through an angle of 10,34" per year, which is the largest motion of any known star. Its radial velocity is v, 67 mi per sec toward the sun. (Source: Zeilik, M., S. Gregory, and E. Smith, Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics, Second Edition, Saunders College Publishing, 1998; Acker, A. and C. Jaschek, Astronomical Methods and Calculations, John Wiley & Sons, 1986.) Not to scale (a) Approximate the tangential velocity v, of Barnard's Star. (Hint: Use the are length formula s = r0.) (b) Compute the magnitude of v.
30. Velocity of a Star The space velocity v of a star relative to the sun can be expressed as the resultant vector of two perpendicular vectors-the radial velocity v, and the tangential velocity v,, where v = v, + v,. If a star is located near the sun and its space velocity is large, then its motion across the sky will also be large. Barnard's Star is a relatively close star with a distance of 35 trillion mi from the sun. It Barnard's Star Sun moves across the sky through an angle of 10,34" per year, which is the largest motion of any known star. Its radial velocity is v, 67 mi per sec toward the sun. (Source: Zeilik, M., S. Gregory, and E. Smith, Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics, Second Edition, Saunders College Publishing, 1998; Acker, A. and C. Jaschek, Astronomical Methods and Calculations, John Wiley & Sons, 1986.) Not to scale (a) Approximate the tangential velocity v, of Barnard's Star. (Hint: Use the are length formula s = r0.) (b) Compute the magnitude of v.
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305652224
Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Chapter7: Triangles
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RP: We mentioned in Section 7.5 that our algebraic treatment of vectors could be attributed, in part, to...
Related questions
Question
I have attached the image of the question with the diagram. This question is from the applications of trigonometry.
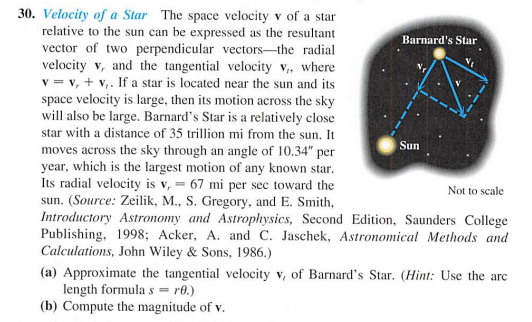
Transcribed Image Text:30. Velocity of a Star The space velocity v of a star
relative to the sun can be expressed as the resultant
vector of two perpendicular vectors-the radial
velocity v, and the tangential velocity v,, where
v = v, + v,. If a star is located near the sun and its
space velocity is large, then its motion across the sky
will also be large. Barnard's Star is a relatively close
star with a distance of 35 trillion mi from the sun. It
Barnard's Star
Sun
moves across the sky through an angle of 10.34" per
year, which is the largest motion of any known star.
Its radial velocity is v, = 67 mi per sec toward the
sun. (Source: Zeilik, M., S. Gregory, and E. Smith,
Introductory Astronomy and Astrophysics, Second Edition, Saunders College
Publishing, 1998; Acker, A. and C. Jaschek, Astronomical Methods and
Calculations, John Wiley & Sons, 1986.)
(a) Approximate the tangential velocity v, of Barnard's Star. (Hint: Use the arc
length formula s = r0.)
(b) Compute the magnitude of v.
Not to scale
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781305652224
Author:
Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. Turner
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning