32 Which one of the following is the general antiderivative G(a), for g(x) Note: CER Select one alternative: 2 OG(z)=4e¹-2 cos(x) + +2m OG(z)=¹+2 cos (2) +√³+0. OG(z)-¹-2 cos(z) +√³+C OG(z)=4e-2 cos(x) + +C VE ¹-2 sin(x) + 4√z?
32 Which one of the following is the general antiderivative G(a), for g(x) Note: CER Select one alternative: 2 OG(z)=4e¹-2 cos(x) + +2m OG(z)=¹+2 cos (2) +√³+0. OG(z)-¹-2 cos(z) +√³+C OG(z)=4e-2 cos(x) + +C VE ¹-2 sin(x) + 4√z?
Intermediate Algebra
10th Edition
ISBN:9781285195728
Author:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Chapter8: Conic Sections
Section8.2: More Parabolas And Some Circles
Problem 63.2PS: By expanding (xh)2+(yk)2=r2, we obtain x22hx+h22ky+k2r2=0. When we compare this result to the form...
Related questions
Question
100%
Plz answer in 10 mints
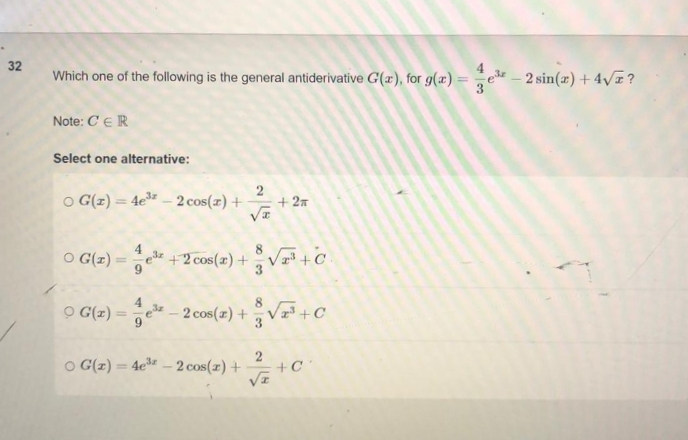
Transcribed Image Text:32
Which one of the following is the general antiderivative G(a), for g(x)=³-2 sin(x) + 4√z?
Note: CER
Select one alternative:
OG(z)=4e³-2 cos(x) +
2
√x
+ 2A
O G(1)
ez
+2 cos(x) +√³+C.
9
0 G(z) = ¹-2 cos(z) +√ + C
OG(x)=4e³-2 cos(x) +
+C
√z
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195728
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285195728
Author:
Jerome E. Kaufmann, Karen L. Schwitters
Publisher:
Cengage Learning