33. Putting a satellite in orbit The strength of Earth's gravitational field varies with the distancer from Earth's center, and the magni- tude of the gravitational force experienced by a satellite of mass m during and after launch is тMG F(r) = p2 Here, M = 5.975 × 10²4 kg is Earth's mass, G = 6.6720 × 10-11 N • m² kg-² is the universal gravitational constant, and r is measured in meters. The work it takes to lift a 1000-kg satellite from Earth's surface to a circular orbit 35,780 km above Earth's center is therefore given by the integral r 35,780,000 1000MG dr joules. Work = 6,370,000 Evaluate the integral. The lower limit of integration is Earth's radi- us in meters at the launch site. (This calculation does not take into account energy spent lifting the launch vehicle or energy spent bringing the satellite to orbit velocity.)
33. Putting a satellite in orbit The strength of Earth's gravitational field varies with the distancer from Earth's center, and the magni- tude of the gravitational force experienced by a satellite of mass m during and after launch is тMG F(r) = p2 Here, M = 5.975 × 10²4 kg is Earth's mass, G = 6.6720 × 10-11 N • m² kg-² is the universal gravitational constant, and r is measured in meters. The work it takes to lift a 1000-kg satellite from Earth's surface to a circular orbit 35,780 km above Earth's center is therefore given by the integral r 35,780,000 1000MG dr joules. Work = 6,370,000 Evaluate the integral. The lower limit of integration is Earth's radi- us in meters at the launch site. (This calculation does not take into account energy spent lifting the launch vehicle or energy spent bringing the satellite to orbit velocity.)
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.6: The Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 94E
Related questions
Question
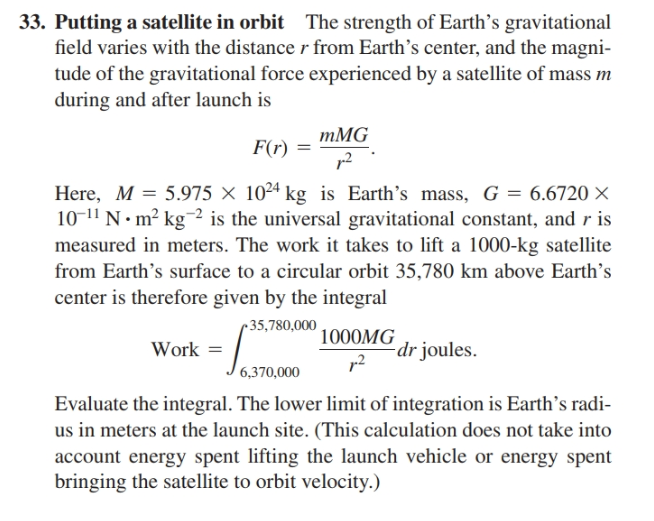
Transcribed Image Text:33. Putting a satellite in orbit The strength of Earth's gravitational
field varies with the distancer from Earth's center, and the magni-
tude of the gravitational force experienced by a satellite of mass m
during and after launch is
тMG
F(r) =
p2
Here, M = 5.975 × 10²4 kg is Earth's mass, G = 6.6720 ×
10-11 N • m² kg-² is the universal gravitational constant, and r is
measured in meters. The work it takes to lift a 1000-kg satellite
from Earth's surface to a circular orbit 35,780 km above Earth's
center is therefore given by the integral
r 35,780,000
1000MG
dr joules.
Work =
6,370,000
Evaluate the integral. The lower limit of integration is Earth's radi-
us in meters at the launch site. (This calculation does not take into
account energy spent lifting the launch vehicle or energy spent
bringing the satellite to orbit velocity.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage