4. A solid has a base that's bounded by y = Vsin(x) and the x- axis from x = 0 to n. The cross-sectional areas perpendicular to the x-axis are half-circles as shown. Set up the integral and solved for the volume based on the Cavalieri-principle %3D co-antians : lalf circles.
4. A solid has a base that's bounded by y = Vsin(x) and the x- axis from x = 0 to n. The cross-sectional areas perpendicular to the x-axis are half-circles as shown. Set up the integral and solved for the volume based on the Cavalieri-principle %3D co-antians : lalf circles.
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Chapter10: Analytic Geometry
Section10.1: The Rectangular Coordinate System
Problem 40E: Find the exact volume of the solid that results when the region bounded in quadrant I by the axes...
Related questions
Question
Need handwritten solution ASAP.
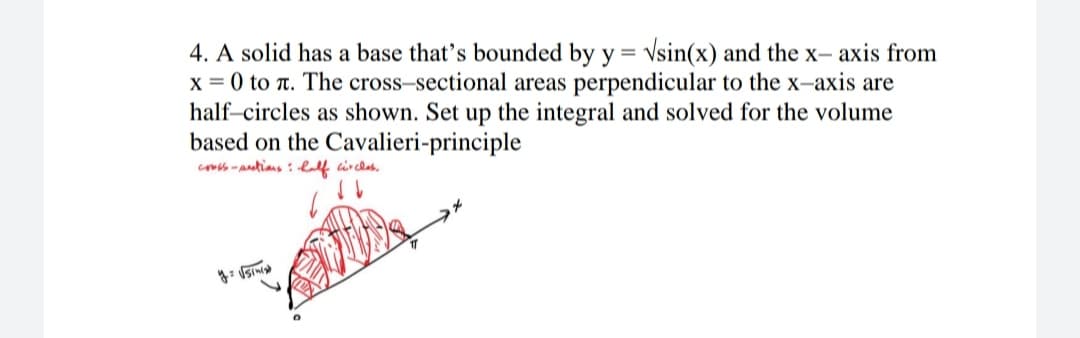
Transcribed Image Text:4. A solid has a base that's bounded by y = Vsin(x) and the x- axis from
x = 0 to T. The cross-sectional areas perpendicular to the x-axis are
half-circles as shown. Set up the integral and solved for the volume
based on the Cavalieri-principle
co -antians : lalf circlas.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning