4. Figure 6 shows a curved surface separating a material with index of refraction n1 from a material with index n2. The surface forms an image I of object 0. The center of curvature is point C.
4. Figure 6 shows a curved surface separating a material with index of refraction n1 from a material with index n2. The surface forms an image I of object 0. The center of curvature is point C.
Related questions
Question
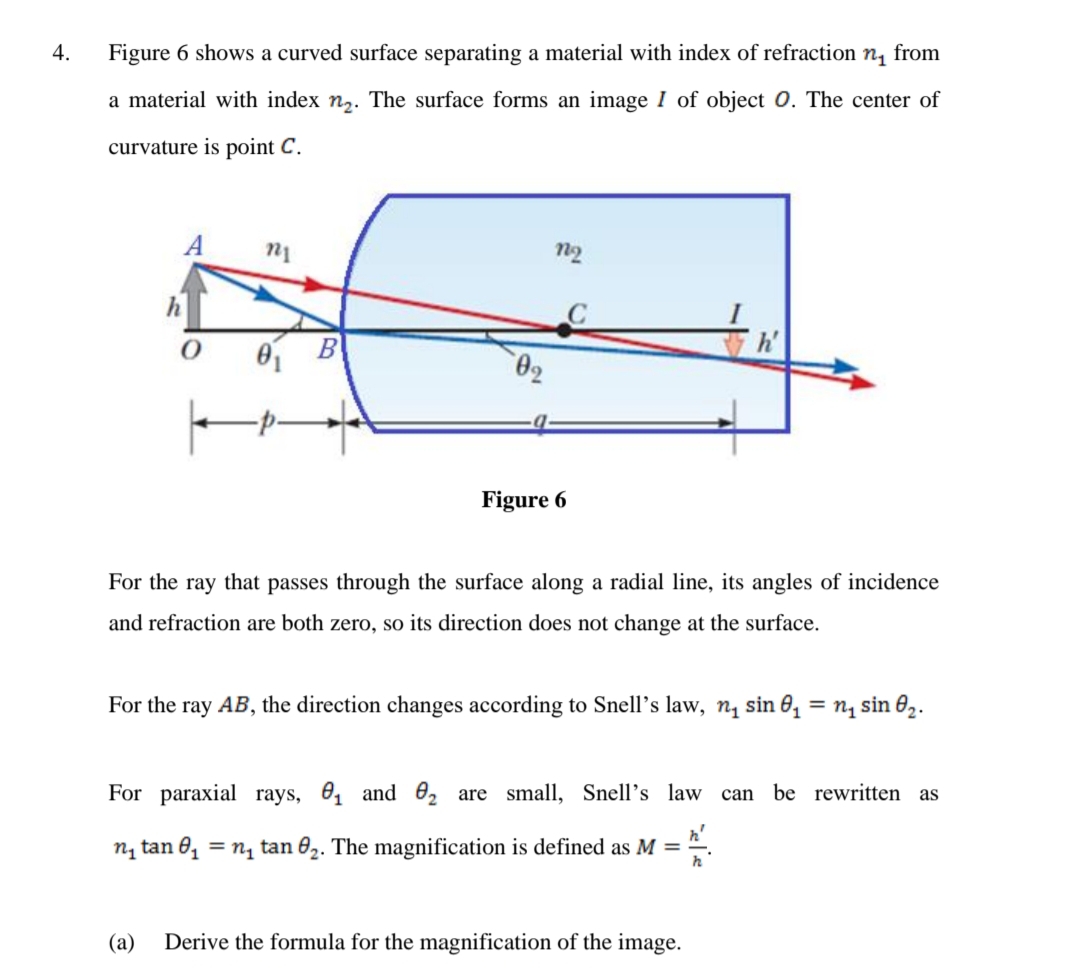
Transcribed Image Text:4.
Figure 6 shows a curved surface separating a material with index of refraction n, from
a material with index n2. The surface forms an image I of object 0. The center of
curvature is point C.
n2
h
B
Figure 6
For the ray that passes through the surface along a radial line, its angles of incidence
and refraction are both zero, so its direction does not change at the surface.
For the ray AB, the direction changes according to Snell’s law, n̟ sin 0,
= n, sin 02.
For paraxial rays, 0, and 02 are small, Snell's law can
be rewritten as
n, tan 6, = n, tan 02. The magnification is defined as M =
(a)
Derive the formula for the magnification of the image.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps
