4. Figure P-130 shows a roof truss and the detail of the riveted connection at joint B. Using allowable stresses of t = 80 MPa and = 120 MPa, how many 20 - mm diameter rivets are required to fasten member BC to the gusset plate? Member BE? What is the largest %3D %3D average tensile or compressive stress in BC and BE?
4. Figure P-130 shows a roof truss and the detail of the riveted connection at joint B. Using allowable stresses of t = 80 MPa and = 120 MPa, how many 20 - mm diameter rivets are required to fasten member BC to the gusset plate? Member BE? What is the largest %3D %3D average tensile or compressive stress in BC and BE?
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
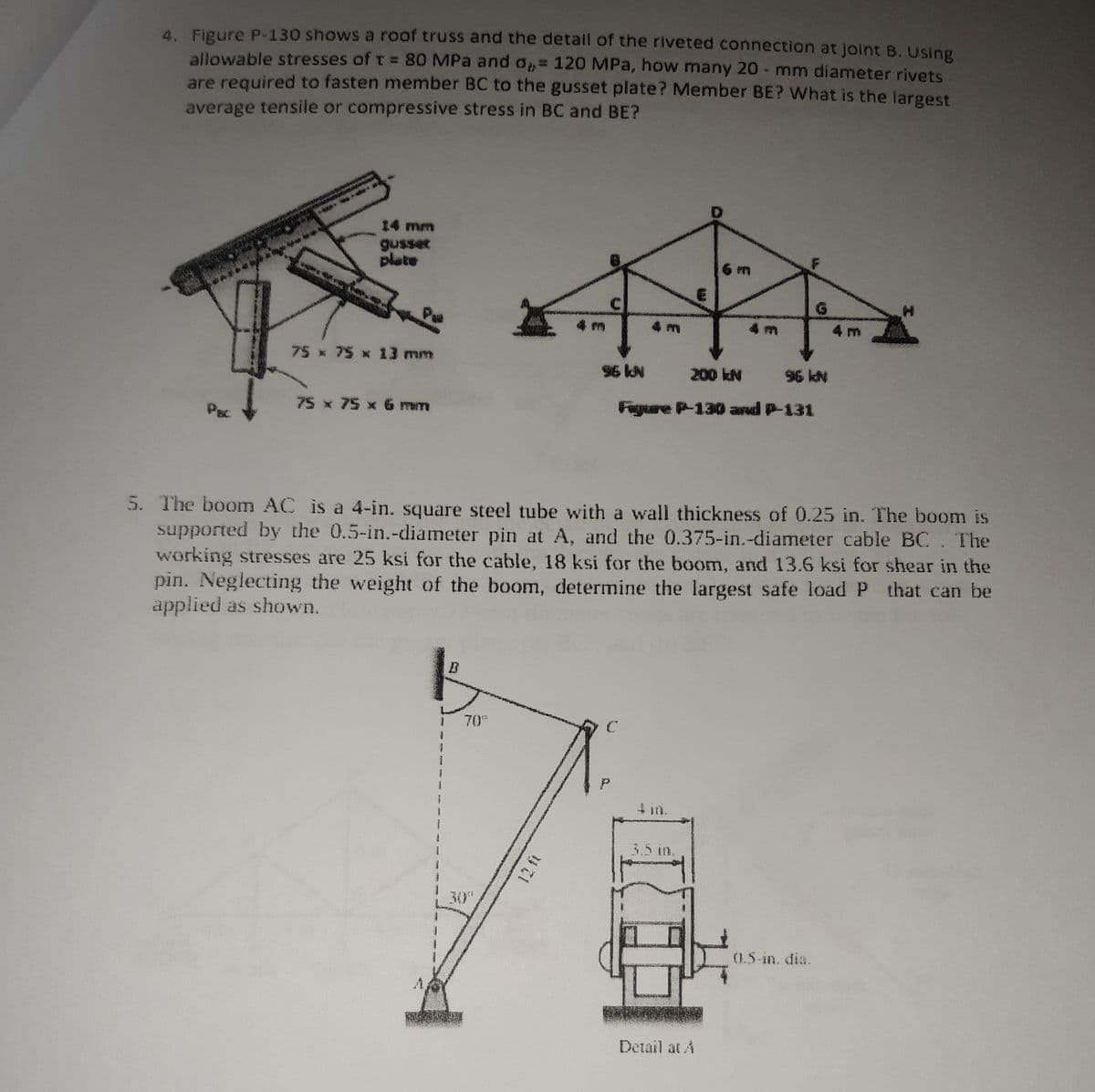
Transcribed Image Text:4. Figure P-130 shows a roof truss and the detail of the riveted connection at joint B. Using
allowable stresses of T = 80 MPa and o= 120 MPa, how many 20 - mm diameter rivets
are required to fasten member BC to the gusset plate? Member BE? What is the largest
average tensile or compressive stress in BC and BE?
14 mm
plate
6 m
C
G.
4 m
75 x 75 x 13 mm
96 kN
200 kN
96 kN
N
75 x 75 x 6 mm
Figure P-130 and P-131
PBC
5. The boom AC is a 4-in. square steel tube with a wall thickness of 0.25 in. The boom is
supported by the 0.5-in.-diameter pin at A, and the 0.375-in.-diameter cable BC. The
working stresses are 25 ksi for the cable, 18 ksi for the boom, and 13.6 ksi for shear in the
pin. Neglecting the weight of the boom, determine the largest safe load P that can be
applied as shown.
70
4 in.
3.5 in.
30
0.5-in. dia.
A.
Detail at A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning