4.) Moment of Inertia About the x-axis Ix 5.) Moment of Inertia About the y – axis Iy 6.) Polar Moment of Inertia about the axes Jo 7.) Moment of Inertia About the centroidal x-axis Ix
4.) Moment of Inertia About the x-axis Ix 5.) Moment of Inertia About the y – axis Iy 6.) Polar Moment of Inertia about the axes Jo 7.) Moment of Inertia About the centroidal x-axis Ix
Chapter2: Loads On Structures
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question
Given:
A1= 3400, A2=800, A3=706.85834, A4=176.71458
Y1=42.5, Y2=26.666, Y3=52.7324, Y4= 62.5
X1=20, X2=53.333, X3=52.7324, X4=17.5
Total Area: 4730.14376
ȳ=40.604
x̄ (x-bar) = 30.6224
Please, I want you to solve the:
4.) Moment of Inertia About the x-axis Ix
5.) Moment of Inertia About the y – axis Iy
6.) Polar Moment of Inertia about the axes Jo
7.) Moment of Inertia About the centroidal x-axis Ix
note: In locating the centroid of the entire section, Varignon's Theorem. Varignon's Theorem locates the centroid of a composite body. I hope you will use the formulas I will be giving.
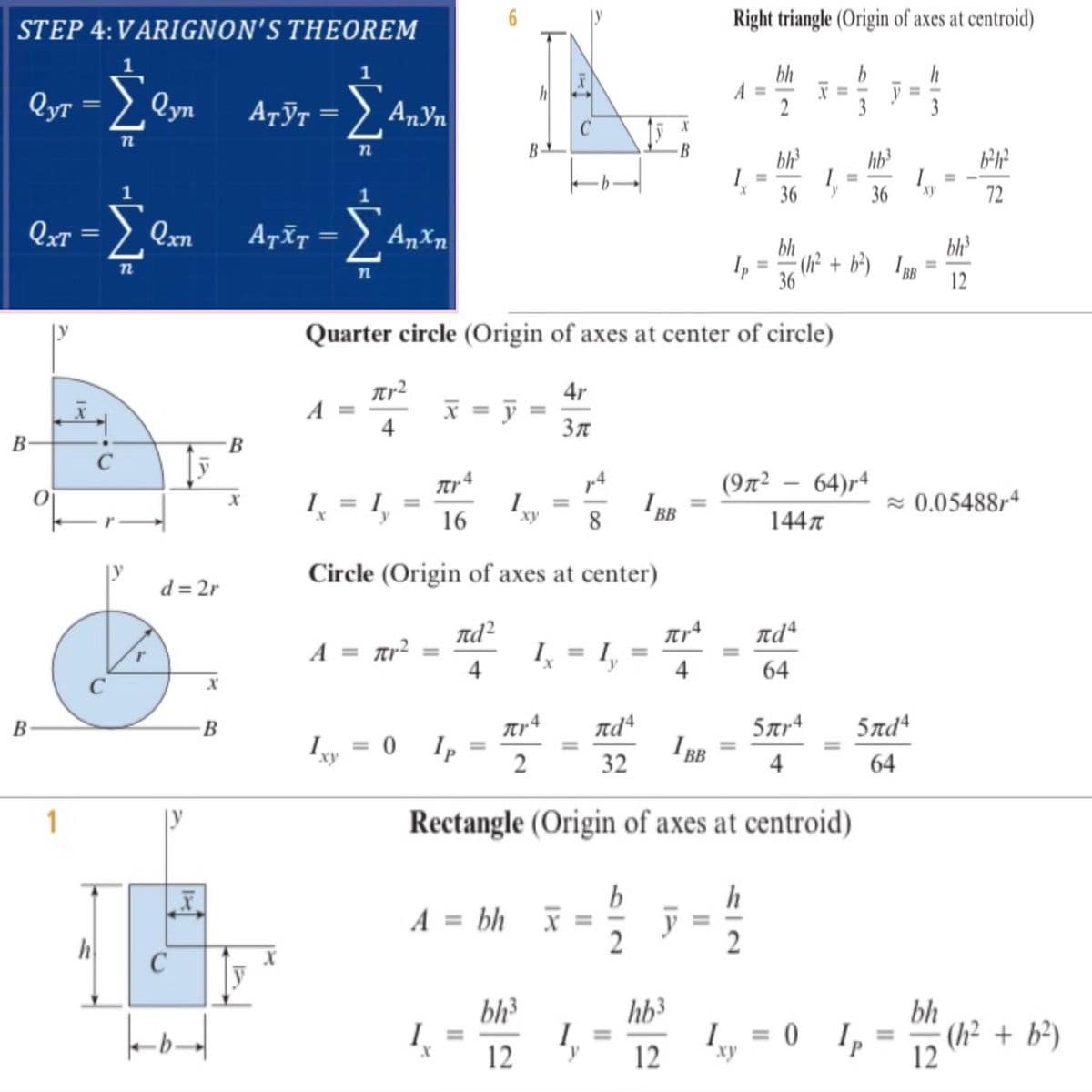
Transcribed Image Text:STEP 4:VARIGNON'S THEOREM
6
Right triangle (Origin of axes at centroid)
1
bh
h
Qyr = 2@yn
Arỹr = >
Anyn
2
3
3
|3D
C
B-
n
bl
hb³
1
36
36
72
Qxt
Qxn
AnXn
%3D
%3D
bl
bh
(h² + b³) I,
36
n
n
12
Quarter circle (Origin of axes at center of circle)
πι
A =
4
4r
x = y
В-
B
C
p4
I, = 1, =
I.
16
(9n² – 64)r4
I BB
= 0.05488,4
8
1447
Circle (Origin of axes at center)
d = 2r
nd²
I, =
nd4
A = tr²
4
4
64
C
ndª
I BB
B-
-B
5ar4
5nd4
Ixy
=0 Ip =
%3D
%3D
ху
2
32
4
64
1
|y
Rectangle (Origin of axes at centroid)
A = bh x
y =
2
h
C
bh³
hb3
bh
I
12
I, = 0 Ip
12
(h² + b?)
12
xy
II
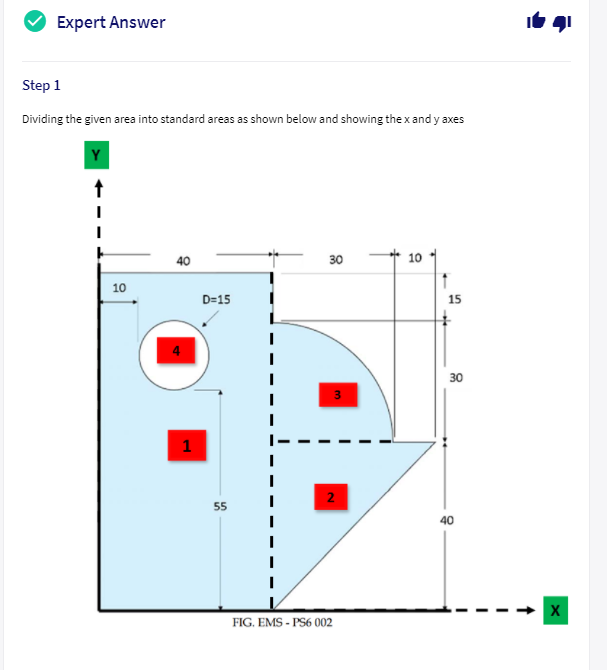
Transcribed Image Text:Expert Answer
Step 1
Dividing the given area into standard areas as shown below and showing the x and y axes
40
30
10
10
D=15
15
30
1
2
55
40
FIG. EMS - PS6 002
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780134610672
Author:
Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:
PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou…
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781337705028
Author:
Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9780073398006
Author:
Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:
9781305156241
Author:
Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning