4. Problem: Prove that in an isosceles triangle the angle bisectors of the congruent angles are congruent.
4. Problem: Prove that in an isosceles triangle the angle bisectors of the congruent angles are congruent.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter7: Distance And Approximation
Section7.4: The Singular Value Decomposition
Problem 51EQ
Related questions
Question
Help with problems 4 & 5 please?

Transcribed Image Text:3:44
1 Spotify
HWK3
PDF - 92 KB
MATH 3713
Fall'20
Homework 3
Due 11-11 at the beginning of class
1. #22 on p.235
2. #25 in Sect. 5.2
3. #26 in Sect. 5.2
4. Problem: Prove that in an isosceles triangle the angle bisectors of the congruent angles are
congruent.
For problem 4 you can certainly use the results already established back in Chapter 4, specifically
Theorems 4.5 and 4.7.
5. In the regular pentagon ABCDE the interior diagonal AC is drawn. What is the degree measure of
angle ZACD?
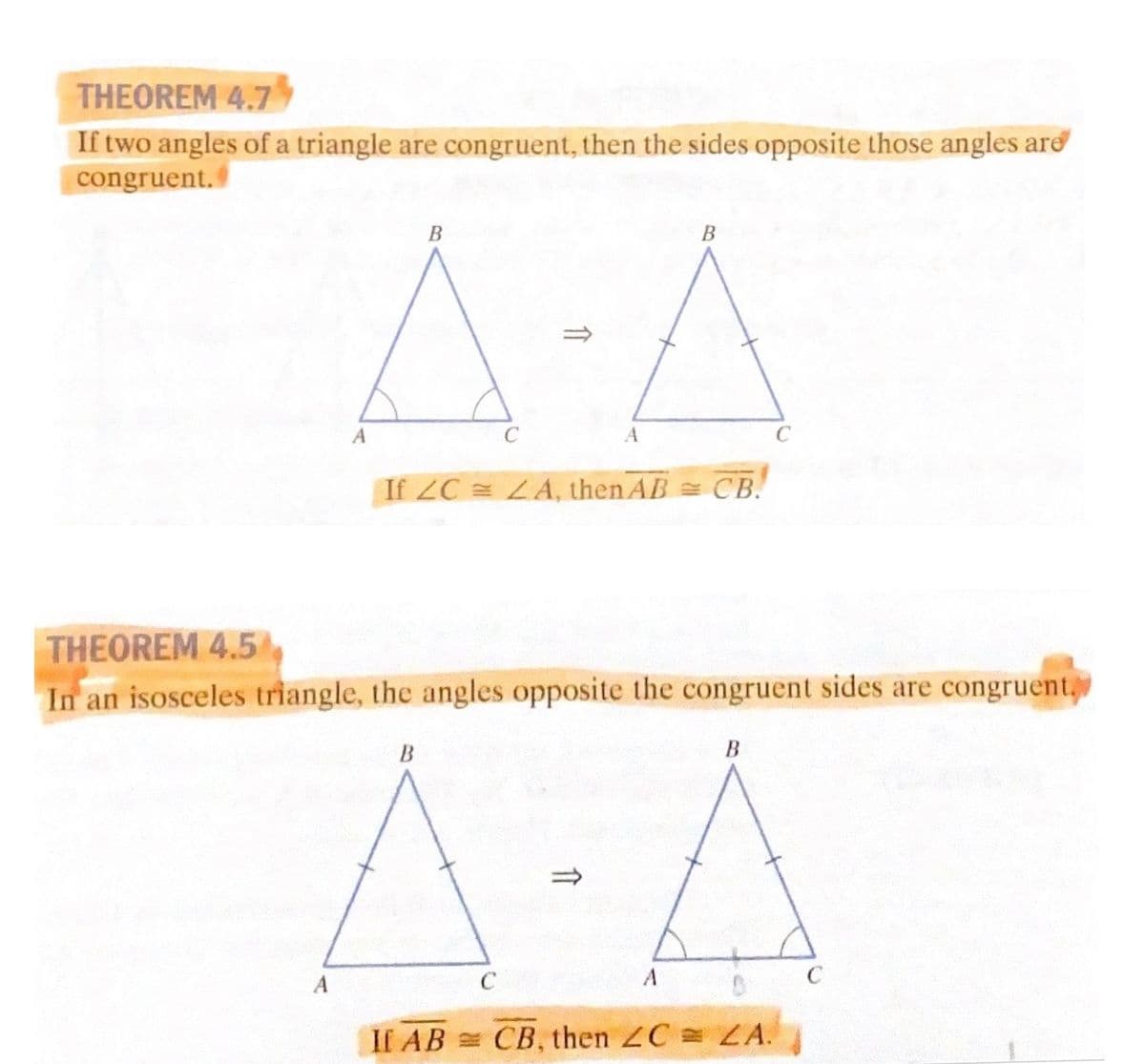
Transcribed Image Text:THEOREM 4.7
If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite those angles ard
congruent.
В
В
A
C
If 2C LA, then AB = CB.
THEOREM 4.5
In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite the congruent sides are congruent,
B
B
A
C
A
If AB CB, then ZC = ZA.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning