5. Coaxial cable. Consider the system of coaxial and concentric charges shown. A long rod carries a uniform linear charge density +A. Surrounding it is an insulating cylindrical shell with inner and outer radius R₁ and R2, respectively, and non-uniform volume charge density p(r) = k/r. where k is a positive constant. A conducting cylindrical shell with inner and outer radius R3 and R₁, respectively, and uniform charge density - surrounds the charged objects as shown. Obtain the electric field in the following regions: (a) in between the rod and insulator (r< R₁), (b) within the insulator (R₁ (R₁). Z= 6. Parallel sheets. Two infinite sheets are placed in the z-axis. One sheet, at z=-a/2, has an insulating material and the other, at z = +a/2, is conducting. Assume that the system is in stable equilibrium. (a) If the insulating sheet has charge q₁ and the conducting sheet has charge 92, what is the electric field at (i) z < -a/2, (ii) z = 0, and (iii) => a/2? (b) How will your answers change if the conducting sheet becomes electrically neutral? conductor insul P(+)
5. Coaxial cable. Consider the system of coaxial and concentric charges shown. A long rod carries a uniform linear charge density +A. Surrounding it is an insulating cylindrical shell with inner and outer radius R₁ and R2, respectively, and non-uniform volume charge density p(r) = k/r. where k is a positive constant. A conducting cylindrical shell with inner and outer radius R3 and R₁, respectively, and uniform charge density - surrounds the charged objects as shown. Obtain the electric field in the following regions: (a) in between the rod and insulator (r< R₁), (b) within the insulator (R₁ (R₁). Z= 6. Parallel sheets. Two infinite sheets are placed in the z-axis. One sheet, at z=-a/2, has an insulating material and the other, at z = +a/2, is conducting. Assume that the system is in stable equilibrium. (a) If the insulating sheet has charge q₁ and the conducting sheet has charge 92, what is the electric field at (i) z < -a/2, (ii) z = 0, and (iii) => a/2? (b) How will your answers change if the conducting sheet becomes electrically neutral? conductor insul P(+)
Related questions
Question
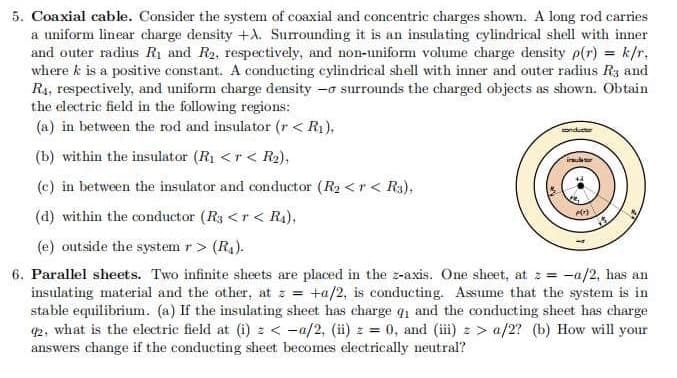
Transcribed Image Text:5. Coaxial cable. Consider the system of coaxial and concentric charges shown. A long rod carries
a uniform linear charge density +A. Surrounding it is an insulating cylindrical shell with inner
and outer radius R₁ and R2, respectively, and non-uniform volume charge density p(r) = k/r.
where k is a positive constant. A conducting cylindrical shell with inner and outer radius R3 and
R₁, respectively, and uniform charge density - surrounds the charged objects as shown. Obtain
the electric field in the following regions:
(a) in between the rod and insulator (r< R₁).
(b) within the insulator (R₁ <r < R₂),
conducter
insul
(c) in between the insulator and conductor (R₂ <r< R3),
(d) within the conductor (R3 <r< R₁),
(e) outside the system r > (R₁).
Z=
6. Parallel sheets. Two infinite sheets are placed in the z-axis. One sheet, at == -a/2, has an
insulating material and the other, at z = +a/2, is conducting. Assume that the system is in
stable equilibrium. (a) If the insulating sheet has charge q₁ and the conducting sheet has charge
92, what is the electric field at (i) z < -a/2, (ii) z = 0, and (iii) => a/2? (b) How will your
answers change if the conducting sheet becomes electrically neutral?
P(+)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images
