5. Let T: P₂ (R) → P₂ (R) be defined as P(ax² +bx+c)=((2a − b)x² + (3a + 3c)x+ (a − 2b - 3c)). Find Ker(T) and Rng(T). Is T an isomorphism? How do you know? If T is an isomorphism, find the inverse of T.
5. Let T: P₂ (R) → P₂ (R) be defined as P(ax² +bx+c)=((2a − b)x² + (3a + 3c)x+ (a − 2b - 3c)). Find Ker(T) and Rng(T). Is T an isomorphism? How do you know? If T is an isomorphism, find the inverse of T.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.5: The Kernel And Range Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 27EQ
Related questions
Question
solve #5 please, Show all of your work on pictures and explain each step you make.
Thank you!
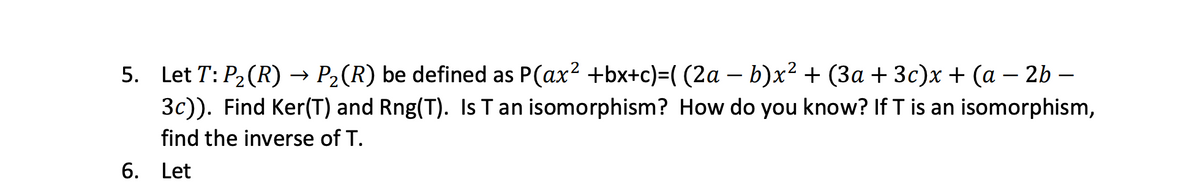
Transcribed Image Text:5. Let T: P₂ (R) → P₂(R) be defined as P(ax² +bx+c)=( (2a − b)x² + (3a + 3c)x + (a − 2b -
3c)). Find Ker(T) and Rng(T). Is T an isomorphism? How do you know? If T is an isomorphism,
find the inverse of T.
6. Let
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,