5. Previously we used the recurrence relation dn+1 = 0.5dn + 200, d₁= 200 and the assumption that dnL to compute the limiting value. Compute L is this way and compare to your answer in 4.
5. Previously we used the recurrence relation dn+1 = 0.5dn + 200, d₁= 200 and the assumption that dnL to compute the limiting value. Compute L is this way and compare to your answer in 4.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.6: Applications And The Perron-frobenius Theorem
Problem 57EQ
Related questions
Question
Only question 5
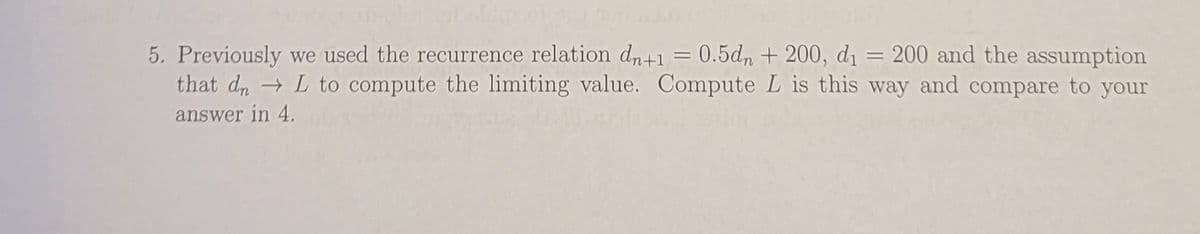
Transcribed Image Text:5. Previously we used the recurrence relation dn+1 = 0.5dn + 200, di = 200 and the assumption
that d, L to compute the limiting value. Compute L is this way and compare to your
%3D
answer in 4.
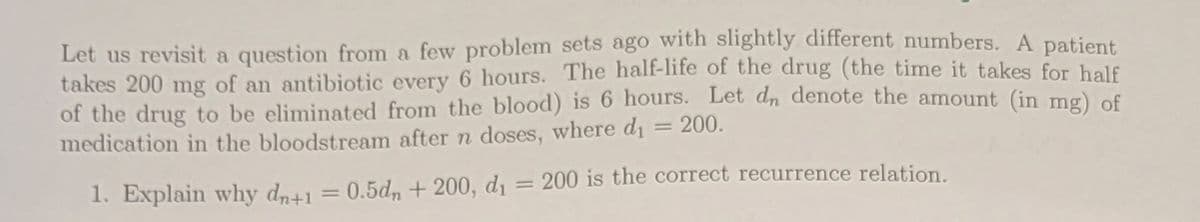
Transcribed Image Text:Let us revisit a question from a few problem sets ago with slightly different numbers. A patient
takes 200 mg of an antibiotic every 6 hours. The half-life of the drug (the time it takes for half
of the drug to be eliminated from the blood) is 6 hours. Let dn denote the amount (in mg) of
medication in the bloodstream after n doses, where dı = 200.
1. Explain why dn+1 = 0.5dn + 200, d1 = 200 is the correct recurrence relation.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning