54. (р^ (~(~рv @)) V (р^@) %3р
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter1: Fundamentals
Section1.1: Sets
Problem 40E: 40. Prove or disprove that .
Related questions
Question
Discrete math. Q49 is an example, and my question is Q54.

Transcribed Image Text:Theorem 2.1.1 Logical Equivalences
Given any statement variables p, q, and r, a tautology t and a contradiction c, the following logical equivalences
hold.
1. Commutative laws:
p^q = q ^p
(p ^ q) ^ r = p ^ (q ^ r)
p^(qv r) = (p ^ q) v (p ^ r)
p^t =p
pv q = q Vp
(p V q) V r = p V (q v r)
p V (q ^ r) = (p v q) ^ (p V r)
2. Associative laws:
3. Distributive laws:
4. Identity laws:
p V c = p
5. Negation laws:
6. Double negative law:
pV ~p = t
~(~p) = p
p^ ~p = c
7. Idempotent laws:
p^p =p
p V p =p
8. Universal bound laws:
p^c = c
~(p V q) = ~p ^~q
p^ (p V q) = p
pvt=t
9. De Morgan's laws:
~(p ^ q) = ~p v~q
10. Absorption laws:
pV (p ^q) = p
11. Negations of t and c:
~t = c
~c = t
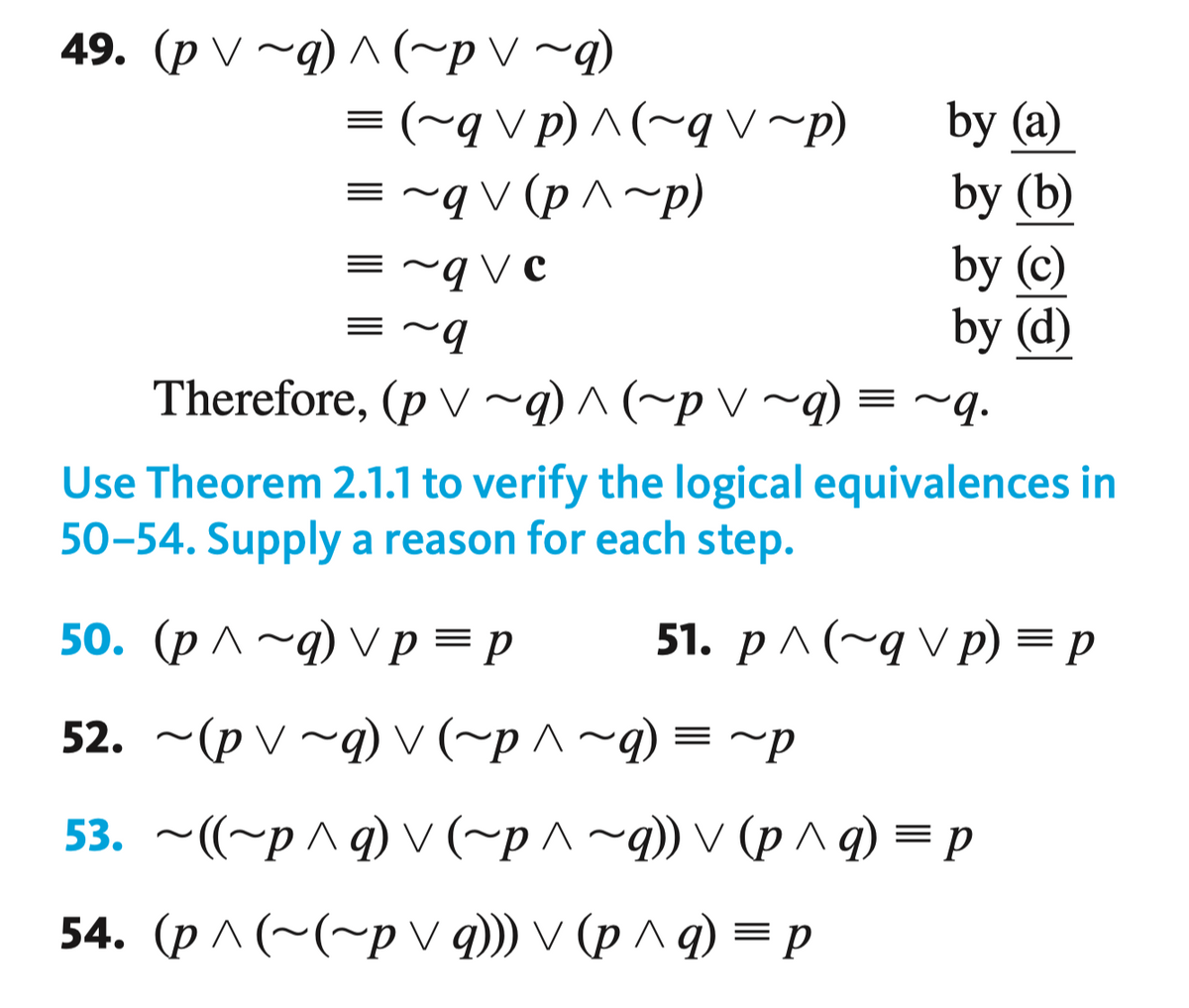
Transcribed Image Text:49. (p V ~q) ^ (~pV ~q)
=(~q v p) ^ (~q v~p)
q V (p ^~p)
by (a)
by (b)
by (c)
by (d)
Therefore, (p V ~q) ^ (~p V ~q) = ~q.
= ~q V ¢
= ~9
Use Theorem 2.1.1 to verify the logical equivalences in
50-54. Supply a reason for each step.
50. (р^~q) vр %3Dр
51. р ^ (~gvр) %—D р
52. ~(p V ~q) V (~p ^~q) = ~p
53. ~((~p ^q) Vv(~p^~q)) V (p ^q) = p
54. (р^ (~(~pvq)) V (р^q) — р
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,