6.16 Some Number Theory in the "Arithmetica" (a) Establish the identities (a² + b?)(c² + d?) = (ac ± bd)2 + (ad + bc)² and use them to express 481 = (13)(37) as the sum of 2 squares in 2 different ways. %3D These identities were given later, in 1202, by Fibonacci in his Liber abaci. They show that the product of 2 numbers, each expressible as the sum of 2 squares, is also expressible as the sum of 2 squares. It can be shown that these identities include the addition formulas for the sine and cosine. The identities later became the germ of the Gaussian theory of arithmetical quadratic forms and of certain developments in modern algebra. (b) Express 1105 = (5)(13)(17) as the sum of 2 squares in 4 different ways. In the following 2 problems, “number" means "positive rational number." %3D (c) If m and n are numbers differing by 1, and if x, y, a are numbers such that x + a = m², y + a = n2, show that xy + a is a square number. (d) If m is any number and x = m2, y = (m + 1)², z = 2(x + y + 1), show that the 6 numbers xy + x + y, yz + y + z, zx + z + x, xy + z, yz + x, zx + y are all square numbers. %3D %3D %3D
6.16 Some Number Theory in the "Arithmetica" (a) Establish the identities (a² + b?)(c² + d?) = (ac ± bd)2 + (ad + bc)² and use them to express 481 = (13)(37) as the sum of 2 squares in 2 different ways. %3D These identities were given later, in 1202, by Fibonacci in his Liber abaci. They show that the product of 2 numbers, each expressible as the sum of 2 squares, is also expressible as the sum of 2 squares. It can be shown that these identities include the addition formulas for the sine and cosine. The identities later became the germ of the Gaussian theory of arithmetical quadratic forms and of certain developments in modern algebra. (b) Express 1105 = (5)(13)(17) as the sum of 2 squares in 4 different ways. In the following 2 problems, “number" means "positive rational number." %3D (c) If m and n are numbers differing by 1, and if x, y, a are numbers such that x + a = m², y + a = n2, show that xy + a is a square number. (d) If m is any number and x = m2, y = (m + 1)², z = 2(x + y + 1), show that the 6 numbers xy + x + y, yz + y + z, zx + z + x, xy + z, yz + x, zx + y are all square numbers. %3D %3D %3D
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter1: Fundamental Concepts Of Algebra
Section1.2: Exponents And Radicals
Problem 92E
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
100%
b-d Please!
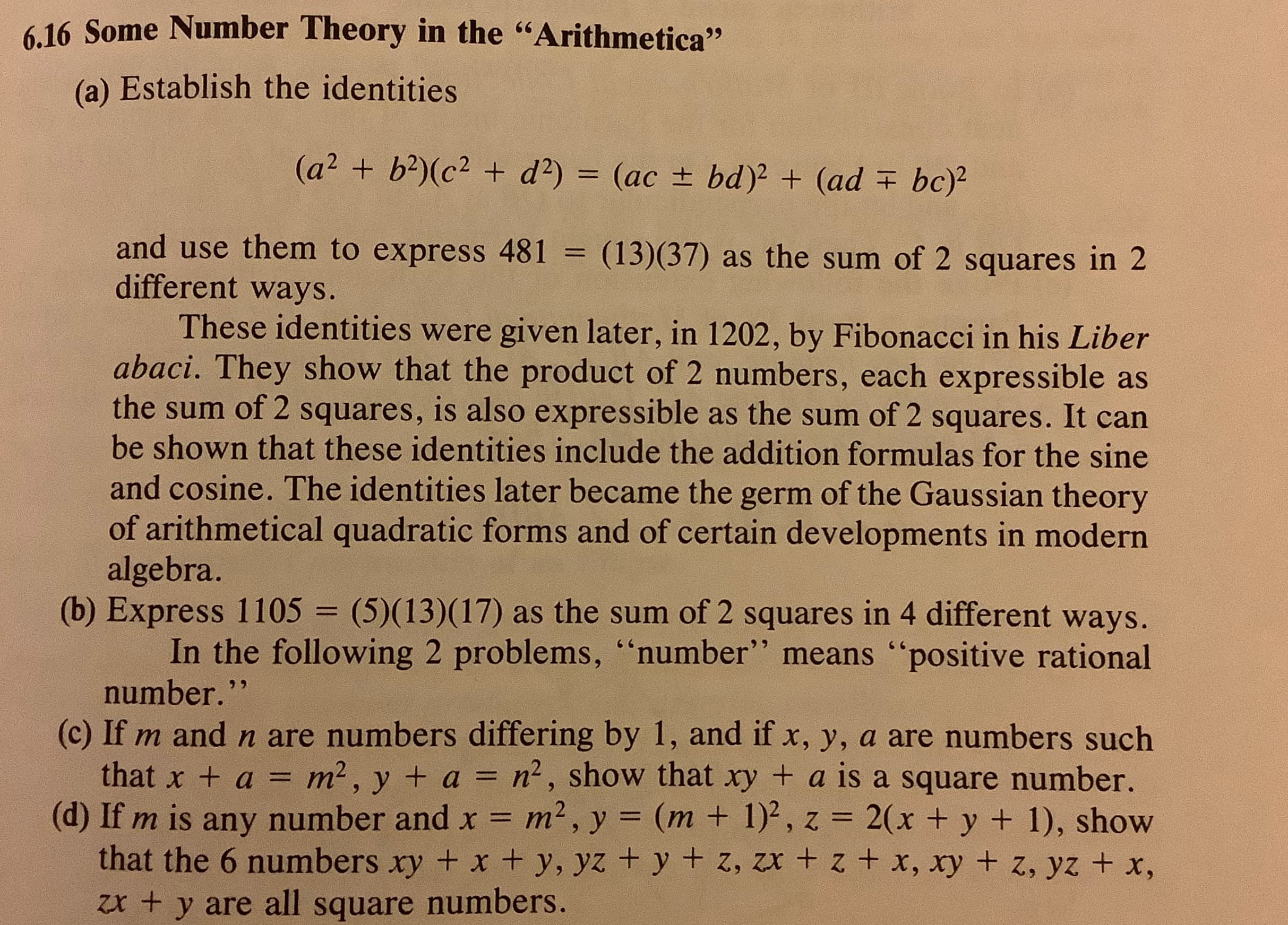
Transcribed Image Text:6.16 Some Number Theory in the "Arithmetica"
(a) Establish the identities
(a² + b?)(c² + d?) = (ac ± bd)2 + (ad + bc)²
and use them to express 481 = (13)(37) as the sum of 2 squares in 2
different ways.
%3D
These identities were given later, in 1202, by Fibonacci in his Liber
abaci. They show that the product of 2 numbers, each expressible as
the sum of 2 squares, is also expressible as the sum of 2 squares. It can
be shown that these identities include the addition formulas for the sine
and cosine. The identities later became the germ of the Gaussian theory
of arithmetical quadratic forms and of certain developments in modern
algebra.
(b) Express 1105 = (5)(13)(17) as the sum of 2 squares in 4 different ways.
In the following 2 problems, “number" means "positive rational
number."
%3D
(c) If m and n are numbers differing by 1, and if x, y, a are numbers such
that x + a = m², y + a = n2, show that xy + a is a square number.
(d) If m is any number and x = m2, y = (m + 1)², z = 2(x + y + 1), show
that the 6 numbers xy + x + y, yz + y + z, zx + z + x, xy + z, yz + x,
zx + y are all square numbers.
%3D
%3D
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage