8-10. A table is a useful tool for writing some inverse functions. When the function has only one x in its equation, the function can be described with a sequence of operations, each applied to the previous result. Consider the following table for f(x) = 2/x-1+3. 1st 2nd 3rd 4th Copy and complete the following table for g(x) if What f Subtracts Multiplies by 2 Adds 3 g(x) = 3(x+1)° – 2. does to x: 1 Since the inverse must undo these operations, in the opposite order, the table for f1(x) would look like the 1st 2nd 3rd 4th What g Adds 1 Divides Subtracts does to x: by 3 one below. What g 1st 2nd 3rd 4th does to x: Subtracts Divides Adds 1 What f-1 does to x: by 2 What is the equation for f'(x)? What is the equation for g (x)? 8-11. Where does the function below
8-10. A table is a useful tool for writing some inverse functions. When the function has only one x in its equation, the function can be described with a sequence of operations, each applied to the previous result. Consider the following table for f(x) = 2/x-1+3. 1st 2nd 3rd 4th Copy and complete the following table for g(x) if What f Subtracts Multiplies by 2 Adds 3 g(x) = 3(x+1)° – 2. does to x: 1 Since the inverse must undo these operations, in the opposite order, the table for f1(x) would look like the 1st 2nd 3rd 4th What g Adds 1 Divides Subtracts does to x: by 3 one below. What g 1st 2nd 3rd 4th does to x: Subtracts Divides Adds 1 What f-1 does to x: by 2 What is the equation for f'(x)? What is the equation for g (x)? 8-11. Where does the function below
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section5.2: Exponential Functions
Problem 31E
Related questions
Concept explainers
Contingency Table
A contingency table can be defined as the visual representation of the relationship between two or more categorical variables that can be evaluated and registered. It is a categorical version of the scatterplot, which is used to investigate the linear relationship between two variables. A contingency table is indeed a type of frequency distribution table that displays two variables at the same time.
Binomial Distribution
Binomial is an algebraic expression of the sum or the difference of two terms. Before knowing about binomial distribution, we must know about the binomial theorem.
Topic Video
Question
8-10

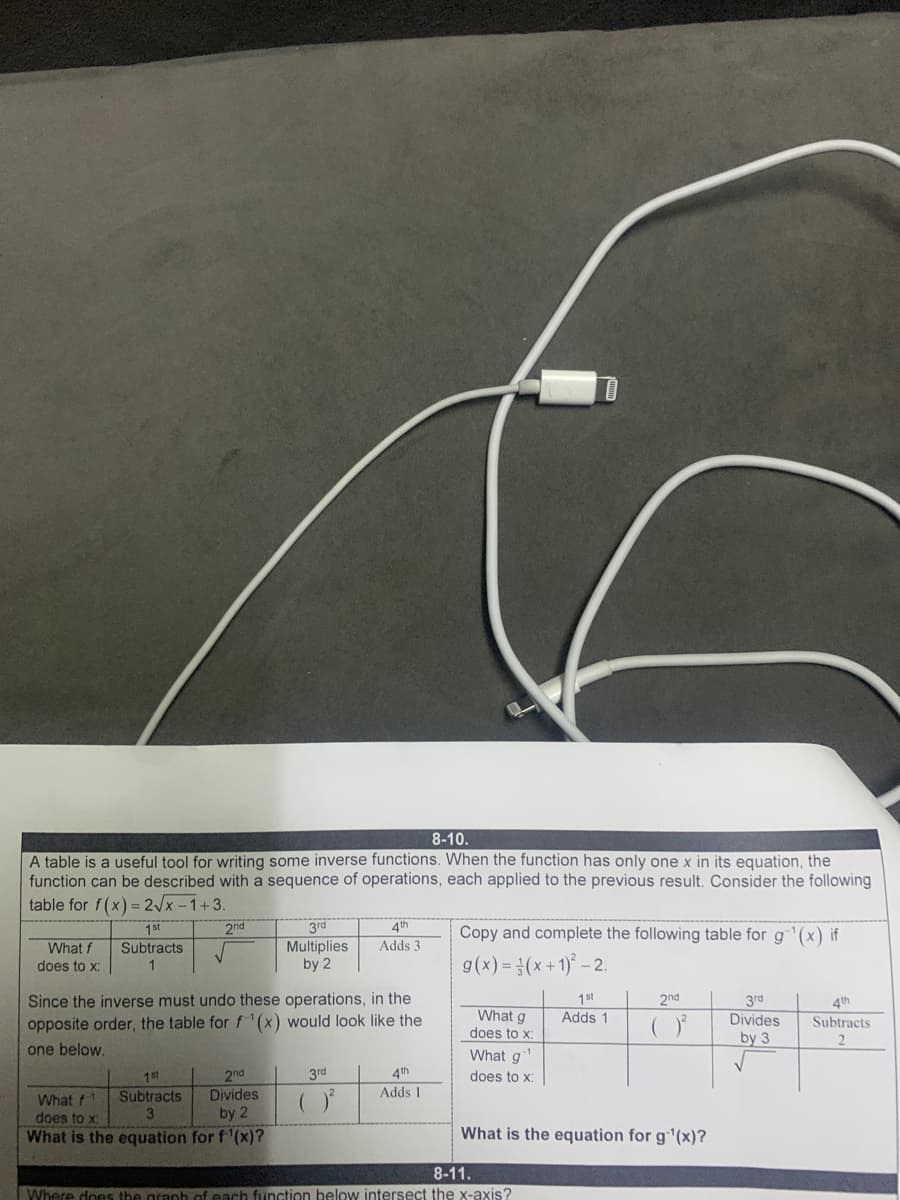
Transcribed Image Text:8-10.
A table is a useful tool for writing some inverse functions. When the function has only one x in its equation, the
function can be described with a sequence of operations, each applied to the previous result. Consider the following
table for f(x) = 2/x -1+3.
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
Copy and complete the following table for g'(x) if
What f
Subtracts
Multiplies
by 2
Adds 3
g(x) = 3(x+1)* – 2.
does to x:
1
Since the inverse must undo these operations, in the
opposite order, the table for f-"(x) would look like the
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
What g
Adds 1
Divides
Subtracts
does to x:
by 3
one below.
What g
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
does to x:
Subtracts
Divides
What f-1
does to x:
What is the equation for f'(x)?
Adds 1
by 2
What is the equation for g1(x)?
8-11.
Where does the
function below
Transcribed Image Text:8-10.
A table is a useful tool for writing some inverse functions. When the function has only one x in its equation, the
function can be described with a sequence of operations, each applied to the previous result. Consider the following
table for f(x) =2/x-1+3.
2nd
1st
Subtracts
4th
3rd
Multiplies
by 2
Copy and complete the following table for g(x) if
What f
Adds 3
g(x) = 3(x+1)° – 2.
does to x:
Since the inverse must undo these operations, in the
opposite order, the table for f '(x) would look like the
1st
Adds 1
2nd
3rd
Divides
4th
What g
Subtracts
does to x:
by 3
2
one below.
What g
4th
2nd
Divides
by 2
What is the equation for f'(x)?
1st
3rd
does to x:
Subtracts
Adds 1
What f
does to x
What is the equation for g'(x)?
8-11.
Where does the granh of each function below intersect the x-axis?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage