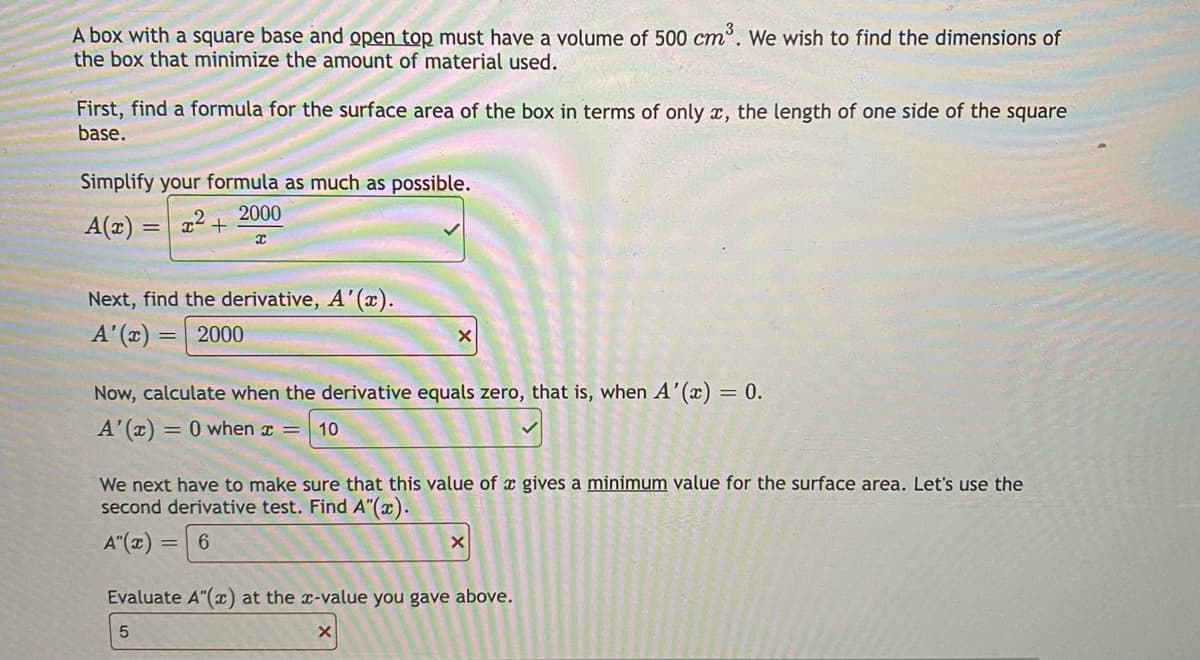
A box with a square base and open top must have a volume of 500 cm. We wish to find the dimensions of the box that minimize the amount of material used. ст First, find a formula for the surface area of the box in terms of only x, the length of one side of the square base. Simplify your formula as much as possible. 2000 A(x) = 2. Next, find the derivative, A'(x). A' (x) : 2000 Now, calculate when the derivative equals zero, that is, when A'(x) = 0. A'(x) = 0 when x = 10 We next have to make sure that this value of x gives a minimum value for the surface area. Let's use the second derivative test. Find A"(x). A"(z) %3D Evaluate A"() at the r-value you gave above.
A box with a square base and open top must have a volume of 500 cm. We wish to find the dimensions of the box that minimize the amount of material used. ст First, find a formula for the surface area of the box in terms of only x, the length of one side of the square base. Simplify your formula as much as possible. 2000 A(x) = 2. Next, find the derivative, A'(x). A' (x) : 2000 Now, calculate when the derivative equals zero, that is, when A'(x) = 0. A'(x) = 0 when x = 10 We next have to make sure that this value of x gives a minimum value for the surface area. Let's use the second derivative test. Find A"(x). A"(z) %3D Evaluate A"() at the r-value you gave above.
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
ChapterA: Appendix
SectionA.2: Geometric Constructions
Problem 10P: A soda can has a volume of 25 cubic inches. Let x denote its radius and h its height, both in...
Related questions
Question
100%
Please help with this answer it's partially wrong, can you please highlight the answers please
Transcribed Image Text:A box with a square base and open top must have a volume of 500 cm. We wish to find the dimensions of
the box that minimize the amount of material used.
First, find a formula for the surface area of the box in terms of only x, the length of one side of the square
base.
Simplify your formula as much as possible.
2000
A(2)
Next, find the derivative, A'(x).
A'(x)
2000
Now, calculate when the derivative equals zero, that is, when A'(x) = 0.
A'(x) = 0 when x =
10
%3D
We next have to make sure that this value of x gives a minimum value for the surface area. Let's use the
second derivative test. Find A"(æ).
A"(x)
6.
Evaluate A"(x) at the x-value you gave above.

Transcribed Image Text:- E A m
QL
Valume of
box . weith square
tox
heighe
Susface area
and
the
box
A =
500 cM3
500
500
AcX) =
2000
ACX) =
A'ix)
-
2o 00
9x3 = o
1o cM
A'cx)
hehen
x = 1 0
A" (x) =
4 00 0
A"(10) =
Arx) iis
minim um
at
x =1ocM
the
box
dlimen Bion of
=10X10 =
8 l0o cM?
Bage
height
5 00
5 cM.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning