A certain computer algorithm executes twice as many operations when it is run with an input of size k as when it is run with an input of size k – 1 (where k is an integer that is greater than 1). When the algorithm is run with an input of size 1, it executes seven operations. How many operations does it execute when it is run with an input of size 28? For each integer n 2 1, let s, be the number of operations the algorithm executes when it is run with an input of size n. Then s, = 7 v and for each integer k 2 1. Therefore, s,, s,, S2, is a geometric sequence V with constant final value x which is 2 . So, for S = every integern2 0, s, = 7 It follows that for an input of size 28, the number of operations executed by the algorithm is s27 which equals 939524096
A certain computer algorithm executes twice as many operations when it is run with an input of size k as when it is run with an input of size k – 1 (where k is an integer that is greater than 1). When the algorithm is run with an input of size 1, it executes seven operations. How many operations does it execute when it is run with an input of size 28? For each integer n 2 1, let s, be the number of operations the algorithm executes when it is run with an input of size n. Then s, = 7 v and for each integer k 2 1. Therefore, s,, s,, S2, is a geometric sequence V with constant final value x which is 2 . So, for S = every integern2 0, s, = 7 It follows that for an input of size 28, the number of operations executed by the algorithm is s27 which equals 939524096
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter2: The Integers
Section2.7: Introduction To Coding Theory (optional)
Problem 12E: Suppose that the check digit is computed as described in Example . Prove that transposition errors...
Related questions
Question
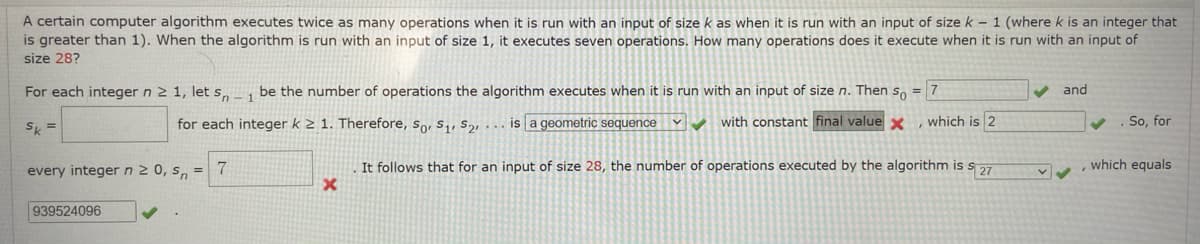
Transcribed Image Text:A certain computer algorithm executes twice as many operations when it is run with an input of size k as when it is run with an input of size k – 1 (where k is an integer that
is greater than 1). When the algorithm is run with an input of size 1, it executes seven operations. How many operations does it execute when it is run with an input of
size 28?
For each integer n 2 1, let s„ be the number of operations the algorithm executes when it is run with an input of size n. Then s, = 7
V and
S, =
for each integer k è 1. Therefore, so, s,, s, . . . is a geometric sequence with constant final valuex
which is 2
V . So, for
every integern2 0, s, =
7
It follows that for an input of size 28, the number of operations executed by the algorithm is
$ 27
which equals
939524096
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,