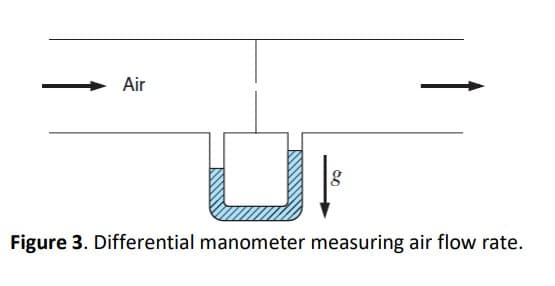
A differential mercury manometer (Figure 3) is being used to measure the air flow rate inside a horizontal tubing. Considering that g = 9.8 m/s2, ρHg = 13,595 − 2.5 T kg/m3(T in Celsius), and T = 10 oC and the height difference is 200 mm, calculate the pressure drop in kPa.
A differential mercury manometer (Figure 3) is being used to measure the air flow rate inside a horizontal tubing. Considering that g = 9.8 m/s2, ρHg = 13,595 − 2.5 T kg/m3(T in Celsius), and T = 10 oC and the height difference is 200 mm, calculate the pressure drop in kPa.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305578296
Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Chapter31: Gas Heat
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 6RQ
Related questions
Question
A differential mercury manometer (Figure 3) is being used to measure the air flow rate inside a horizontal tubing. Considering that g = 9.8 m/s2, ρHg = 13,595 − 2.5 T kg/m3(T in Celsius), and T = 10 oC and the height difference is 200 mm, calculate the pressure drop in kPa.
Transcribed Image Text:Air
Figure 3. Differential manometer measuring air flow rate.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning