a) Find the matrix A. Hint: A = PDP!, Note: you don't need to know A for the rest of this problem. b) Sketch the trajectories of this dynamical system, including at least one trajectory with each kind of behavior. Include all special trajectories (i.e. trajectories of eigenvectors). Trajectories should have arrows indicating direction (as k increases). c) Classify the origin as a stable or unstable equilibrium. Classify the system as a node or saddle. Alternatively, if vou prefer, vou can use the book's nomenclature: classify the origin
a) Find the matrix A. Hint: A = PDP!, Note: you don't need to know A for the rest of this problem. b) Sketch the trajectories of this dynamical system, including at least one trajectory with each kind of behavior. Include all special trajectories (i.e. trajectories of eigenvectors). Trajectories should have arrows indicating direction (as k increases). c) Classify the origin as a stable or unstable equilibrium. Classify the system as a node or saddle. Alternatively, if vou prefer, vou can use the book's nomenclature: classify the origin
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
Chapter7: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section7.1: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Problem 79E
Related questions
Question
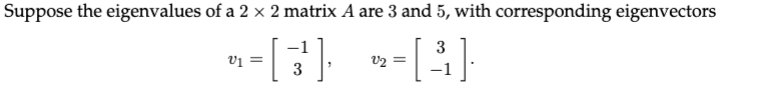
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the eigenvalues of a 2 x 2 matrix A are 3 and 5, with corresponding eigenvectors
3
= la
3
-1

Transcribed Image Text:a) Find the matrix A. Hint: A = PDP !. Note: you don't need to know A for the rest of this
problem.
b) Sketch the trajectories of this dynamical system, including at least one trajectory with each
kind of behavior. Include all special trajectories (i.e. trajectories of eigenvectors). Trajectories
should have arrows indicating direction (as k increases).
c) Classify the origin as a stable or unstable equilibrium. Classify the system as a node or
saddle. Alternatively, if you prefer, you can use the book's nomenclature: classify the origin
as an attractor (stable node), repeller (unstable node), or saddle point.
d) Pick a random point (not on a special trajectory) to be ro, and describe the behavior of xk as
k → 00, and as k → -0o. (See parenthetical in 4.F.1.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning