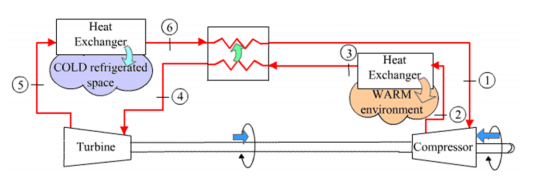
A gas refrigeration system using air as the working fluid has a pressure ratio of 5 (see Fig. Q 1). Air enters the compressor at 0°C. The high-pressure air is cooled to 35 C o by rejecting heat to the surroundings. The refrigerant leaves the turbine at 80 C o and enters the refrigerated space where it- absorbs heat before entering the regenerator. The mass flow rate of air is 0.4 kg/s . Assuming isentropic efficiencies of 0.8 for the compressor and 0.85 for the turbine and variable specific heats. Draw accurately the cycle on a T-s diagram with properly labelled property values. Determine (a) the effectiveness of the regenerator, (b) the rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space, and (c) the COP of the cycle.
A gas refrigeration system using air as the working fluid has a pressure ratio of 5 (see Fig. Q 1). Air enters the compressor at 0°C. The high-pressure air is cooled to 35 C o by rejecting heat to the surroundings. The refrigerant leaves the turbine at 80 C o and enters the refrigerated space where it- absorbs heat before entering the regenerator. The mass flow rate of air is 0.4 kg/s . Assuming isentropic efficiencies of 0.8 for the compressor and 0.85 for the turbine and variable specific heats. Draw accurately the cycle on a T-s diagram with properly labelled property values. Determine
(a) the effectiveness of the regenerator,
(b) the rate of heat removal from the refrigerated space, and
(c) the COP of the cycle. Also, determine
(d) the refrigeration load and the COP if this system operated on the simple gas refrigeration cycle. Use the same compressor inlet temperature as given, the same turbine inlet temperature as calculated, and the same compressor and turbine efficiencies. Draw the T-s diagram for this simple case also
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 6 steps with 1 images


