A gauge # 10 HSLA steel for an automotive application has a Young’s modulus of 200 GPa, a yield strength of 370 MPa and a ultimate tensile strength of 440 MPa. What is the punch force needed to punch a square hole with a side length of 20 mm on this HSLA steel? Show your work.
A gauge # 10 HSLA steel for an automotive application has a Young’s modulus of 200 GPa, a yield strength of 370 MPa and a ultimate tensile strength of 440 MPa. What is the punch force needed to punch a square hole with a side length of 20 mm on this HSLA steel? Show your work.
Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course List)
2nd Edition
ISBN:9781285444543
Author:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Chapter3: Job Planning, Benchwork, And Layout
Section3.1: Understanding Drawings
Problem 1RQ: Information such as tolerances and scale can be found in the________ of an engineering drawing.
Related questions
Question
A gauge # 10 HSLA steel for an automotive application has a Young’s modulus of 200 GPa, a yield strength of 370 MPa and a ultimate tensile strength of 440 MPa. What is the punch force needed to punch a square hole with a side length of 20 mm on this HSLA steel? Show your work.
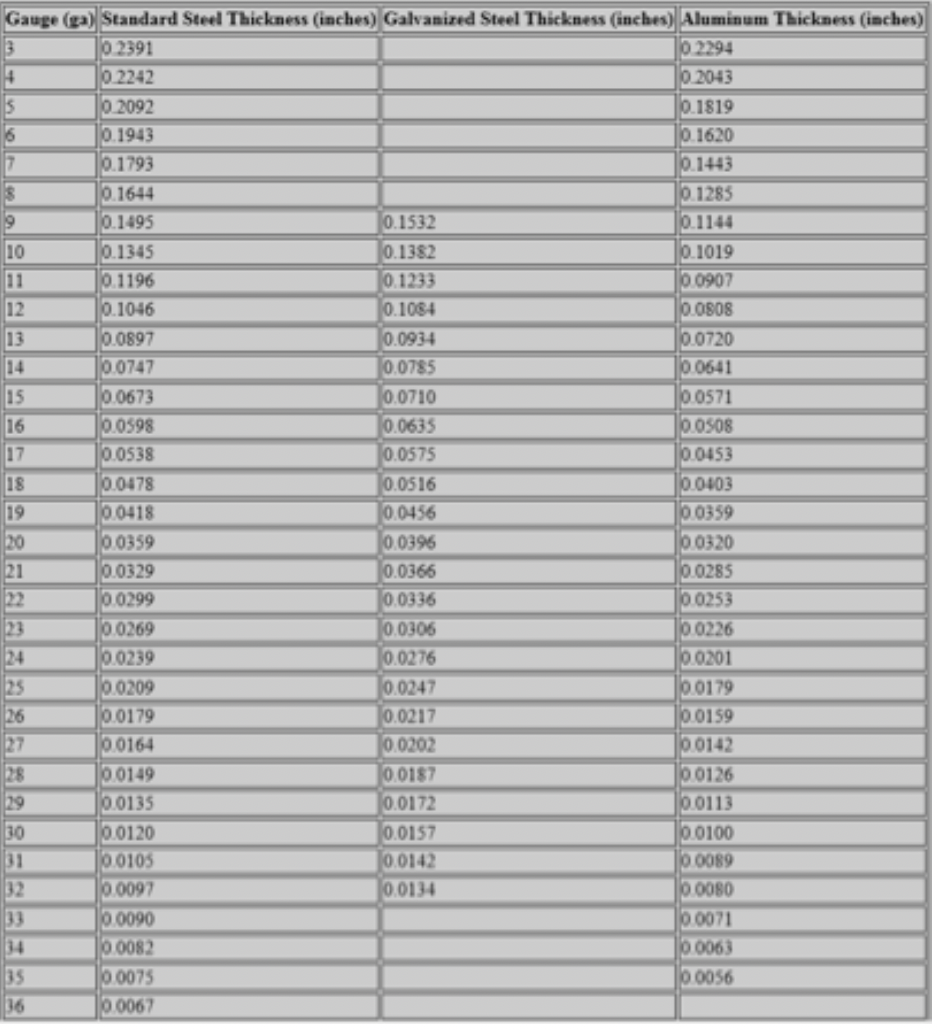
Transcribed Image Text:Gauge (ga) Standard Steel Thickness (inches) Galvanized Steel Thickness (inches) Aluminum Thickness (inches)
0.2391
0.2242
0.2092
0.1943
0.1793
0.2294
0.2043
4.
0.1819
0.1620
7
0.1443
0.1285
0.1644
0.1495
0.1532
0.1144
10
0.1345
0.1196
0.1046
0.1019
0.0907
0.1382
11
12
0.1233
0.1084
8080 0
0.0720
0.0897
0.0747
0.0673
0.0934
0.0785
0.0710
0.0635
0.0575
0.0516
0.0456
13
0.0641
0.0571
0.0508
0.0453
14
15
0.0598
0.0538
16
17
0.0478
0.0403
0.0359
18
19
0.0418
20
0.0359
0.0396
0.0366
0.0336
0.0306
0.0276
0.0247
0.0217
0.0202
0.0320
0.0285
0.0253
21
0.0329
22
0.0299
0.0269
0.0239
0.0209
0.0179
23
0.0226
24
0.0201
25
26
27
0.0179
0.0159
0.0142
0.0126
0.0164
00149
0.0135
28
0.0187
29
0.0172
0.0113
0.0120
0.0105
0.0097
0.0090
0.0100
0 0089
0.0080
0.0071
0.0063
30
31
32
33
0.0157
0.0142
0.0134
34
0.0082
0.0075
0.0067
35
o 0056
36
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285444543
Author:
Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Precision Machining Technology (MindTap Course Li…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781285444543
Author:
Peter J. Hoffman, Eric S. Hopewell, Brian Janes
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305578296
Author:
John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill Johnson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning