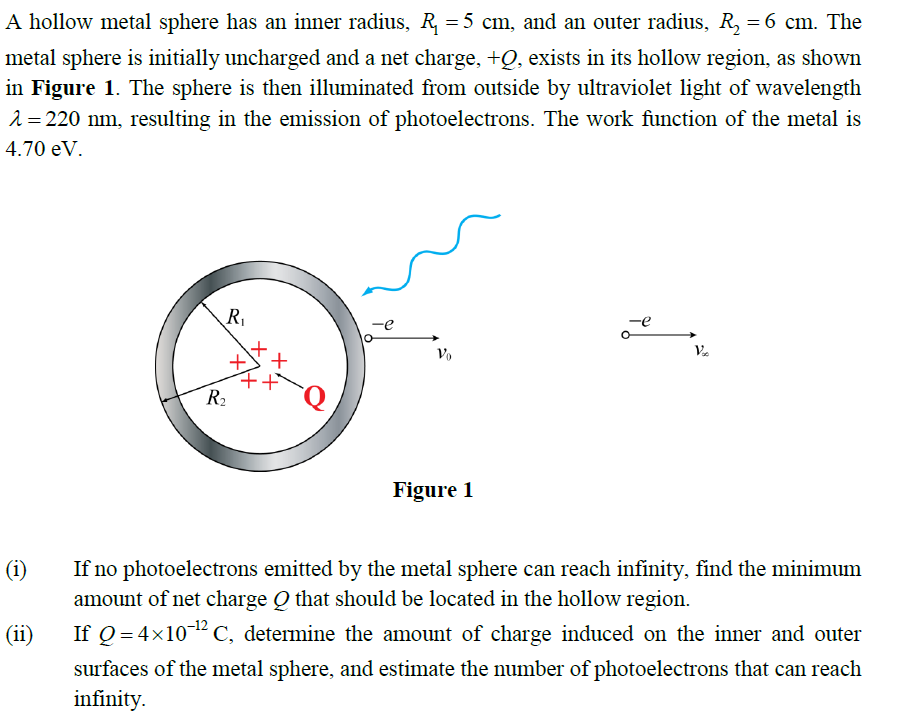
A hollow metal sphere has an inner radius, R = 5 cm, and an outer radius, R, = 6 cm. The metal sphere is initially uncharged and a net charge, +Q, exists in its hollow region, as shown in Figure 1. The sphere is then illuminated from outside by ultraviolet light of wavelength 2 = 220 nm, resulting in the emission of photoelectrons. The work function of the metal is 4.70 eV. R, R2 Figure 1 (i) If no photoelectrons emitted by the metal sphere can reach infinity, find the minimum amount of net charge Q that should be located in the hollow region. (ii) If Q = 4×102C, determine the amount of charge induced on the inner and outer surfaces of the metal sphere, and estimate the number of photoelectrons that can reach infinity.
A hollow metal sphere has an inner radius, R1=5cm, and an outer radius,
R2=6cm. The metal sphere is initially uncharged and a net charge, +Q, exists in its hollow region, as shown in Figure 1. The sphere is then illuminated from outside by ultraviolet light of wavelength 220 nm, resulting in the emission of photoelectrons. The work function of the metal is 4.70 eV.
(i) If no photoelectrons emitted by the metal sphere can reach infinity, find the minimum amount of net charge Q that should be located in the hollow region.
(ii) If Q=4*10-12 C, determine the amount of charge induced on the inner and outer surfaces of the metal sphere, and estimate the number of photoelectrons that can reach infinity.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images









